Introduction
The process of building APEX applications always begins with a fundamental step—having tables in your database schema. These tables form the foundation of your application, defining how data is stored, managed, and accessed.
But simply having tables isn’t enough. A well-designed schema is critical to ensure the scalability, performance, and maintainability of your application. Developers must follow principles like database normalization to eliminate redundancy, ensure data integrity, and structure data efficiently. They also need to address database design intricacies, such as defining proper primary and foreign keys, creating appropriate indexes, and ensuring that relationships between entities are properly captured.
Designing such a schema requires significant database expertise. Developers need a deep understanding of relational modelling principles and best practices to ensure the schema not only meets immediate application requirements but also scales gracefully for future needs.
But what if this foundational task could be simplified?
With Generative Development (GenDev) powered by AI re-defining the APEX developer’s toolkit—helping to write and debug code using APEX Assistant in code editors, and even create entire APEX applications—why not extend its power to schema design? Enter Oracle APEX 24.2’s newest feature: Create Data Model Using AI.
Create Data Model Using AI – Feature Overview
Some of the key highlights of the Create Data Model Using AI are:
- Schema Creation with AI: You can design an entire application schema by providing high-level requirements
- Uses Generative AI Service: Leverages the Generative AI service to design data models.
- Output Formats: You can generate schemas in two formats : Oracle SQL and Quick SQL.
- Synthetic Data Generation: You can also generate contextually accurate sample data for your data model to assist with testing and prototyping.
Use Case: Online Learning Platform
In this blog post, we will be designing a data model for an Online Learning Platform using AI.
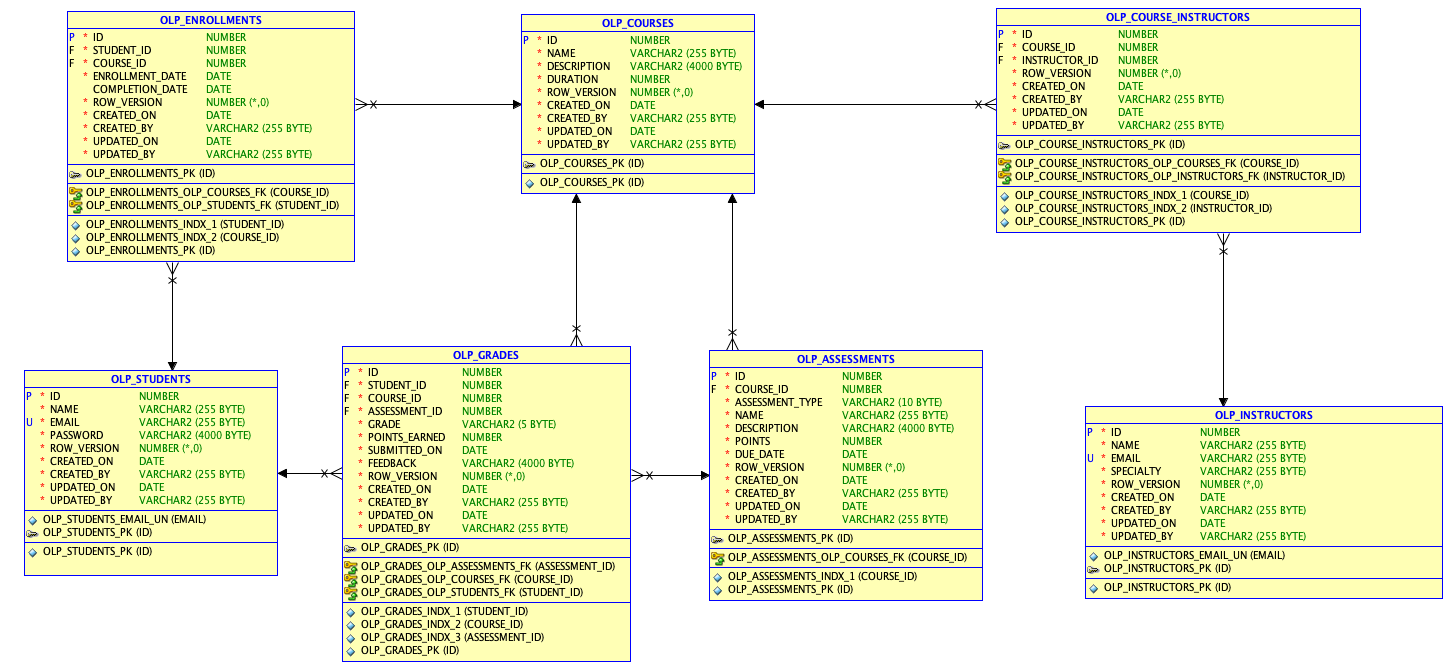
Let’s dive right in!
Prerequisite: Create Generative AI Service
First, we need to set up a Generative AI Service to help us generate data models. To create one, navigate to Workspace Utilities > Generative AI Service and click Create. In this demo, we will use OCI Generative AI Service as the AI Provider and the meta.llama-3.2-90b-vision-instruct. This feature works well with any AI Provider and model of your choice.
Ensure the Used by App Builder switch is turned on. This activates Generative AI features within the Workspace. If the Generative AI features are not visible in the Workspace, it’s likely because the Used by App Builder switch is not enabled for your Generative AI Service.
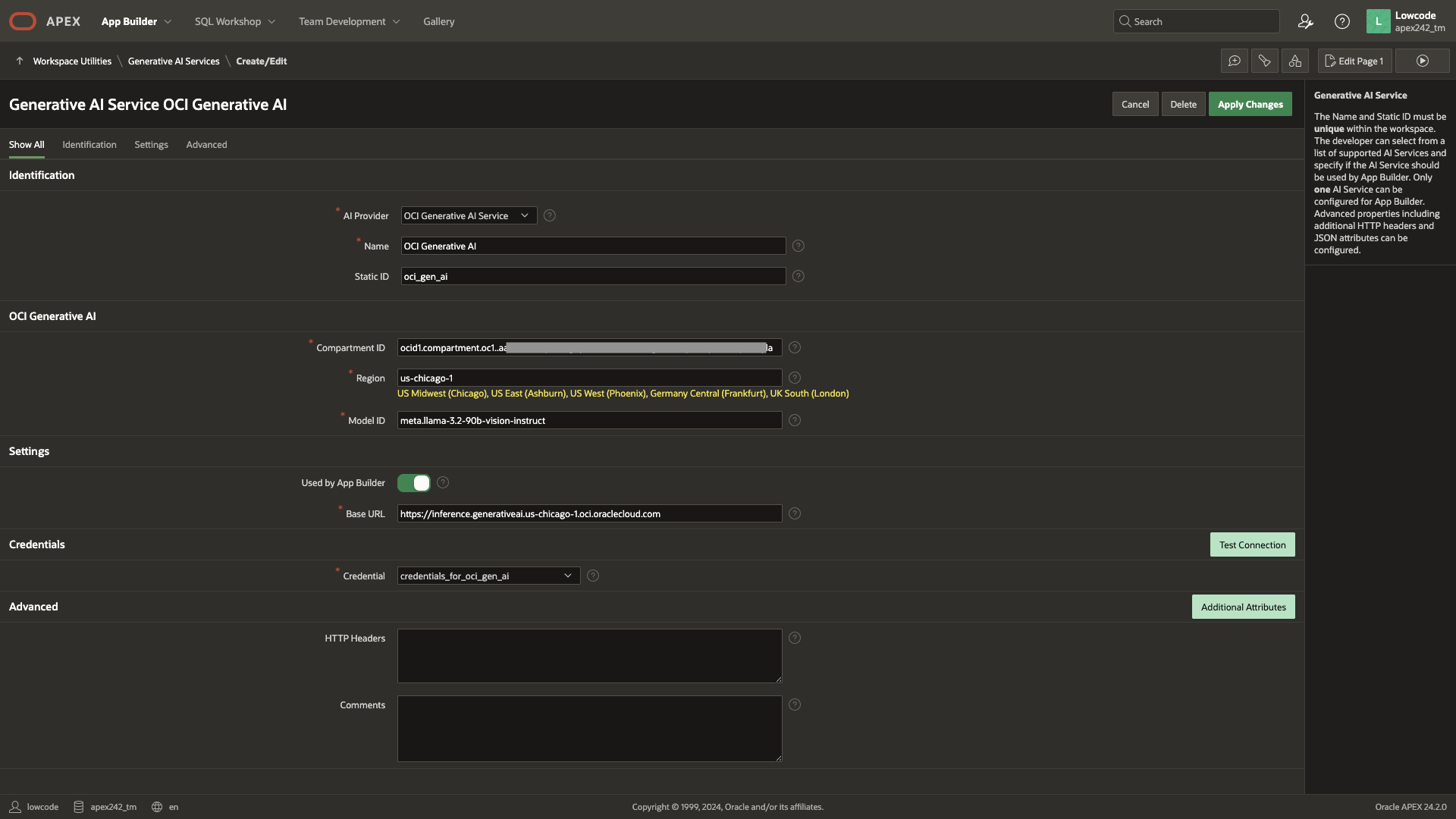
With that complete, let’s move on to designing the data model for the Online Learning Platform.
Data Modelling Using AI
The Create Data Model Using AI Option is available under SQL Workshop > Utilities. You can also access it directly from the SQL Workshop Home Page under Tasks (right section).
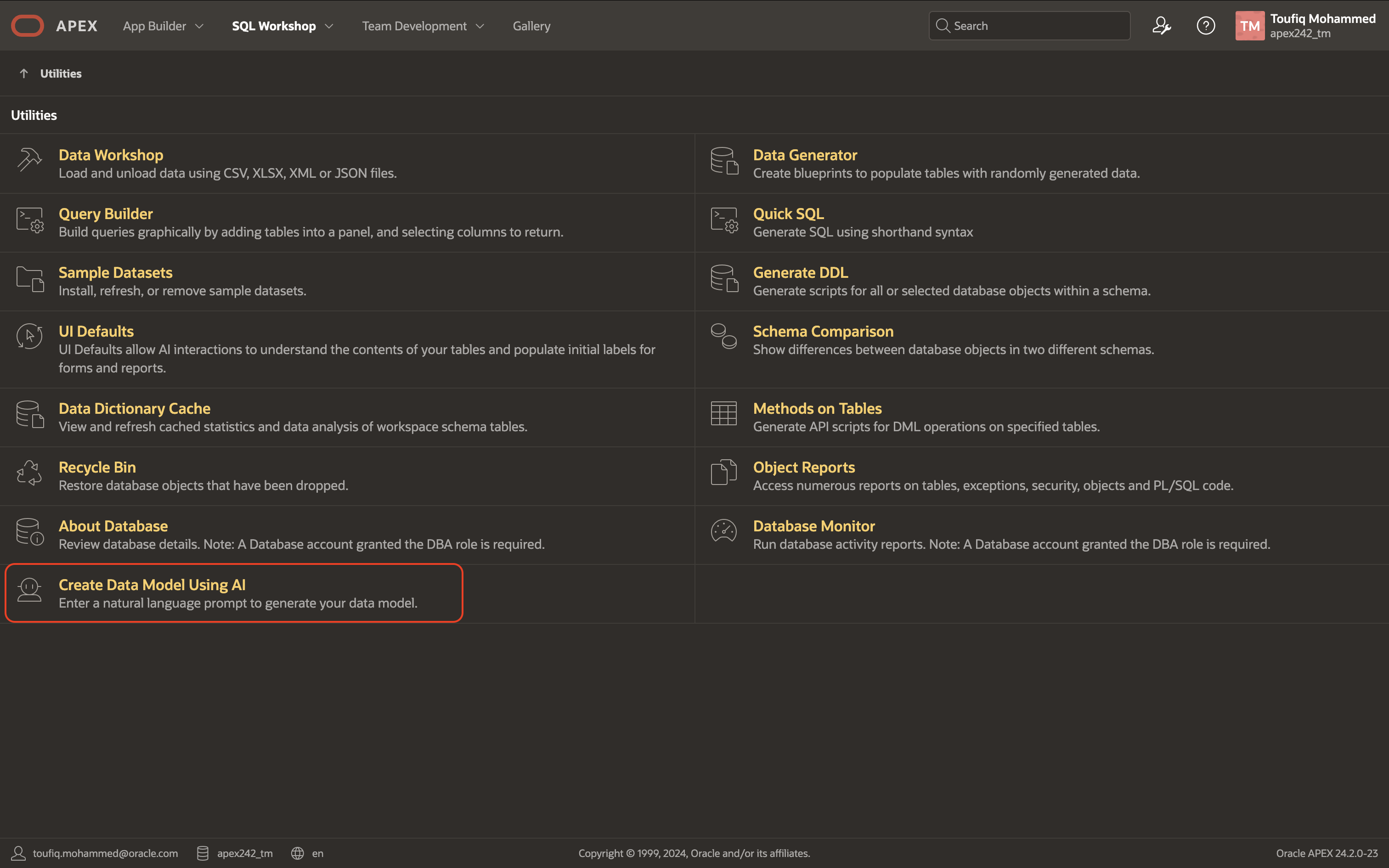
Clicking this link opens the APEX Assistant, which closely resembles the APEX Assistant used for generating APEX applications using Generative AI (introduced in version 24.1).
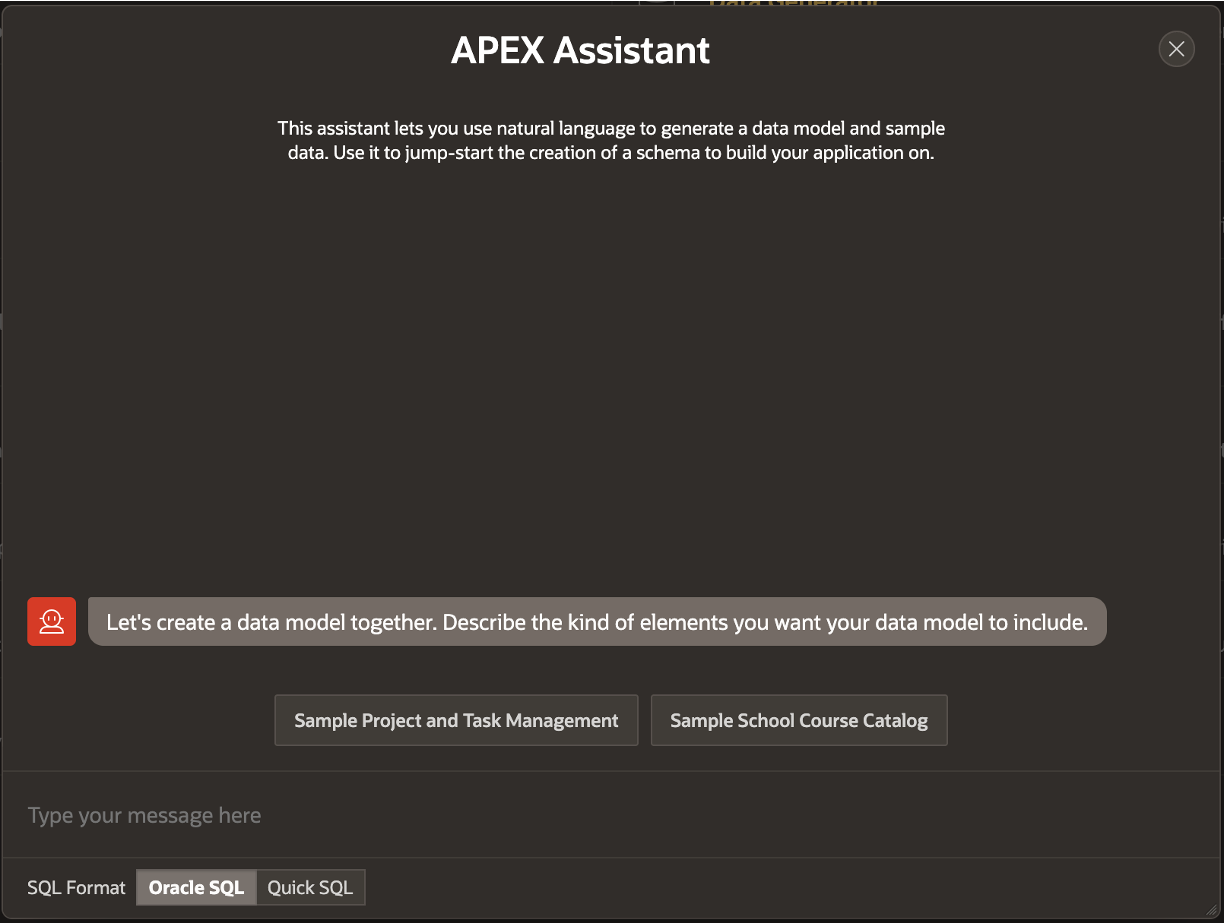
A key attribute in the APEX Assistant dialog is the SQL Format switch, which lets you generate the data model in two formats:
- Oracle SQL: Produces DDL in Oracle SQL format to create the necessary tables, indexes, and other objects.
- Quick SQL: Generates the data model in Quick SQL shorthand syntax, which can later be converted into Oracle SQL to create the required database objects.
Let’s start with the Oracle SQL option.
I provide the following prompt: “Create a data model for an online learning platform with entities like students, courses, and instructors.” The APEX Assistant promptly generates a response containing the necessary SQL to create the data model.
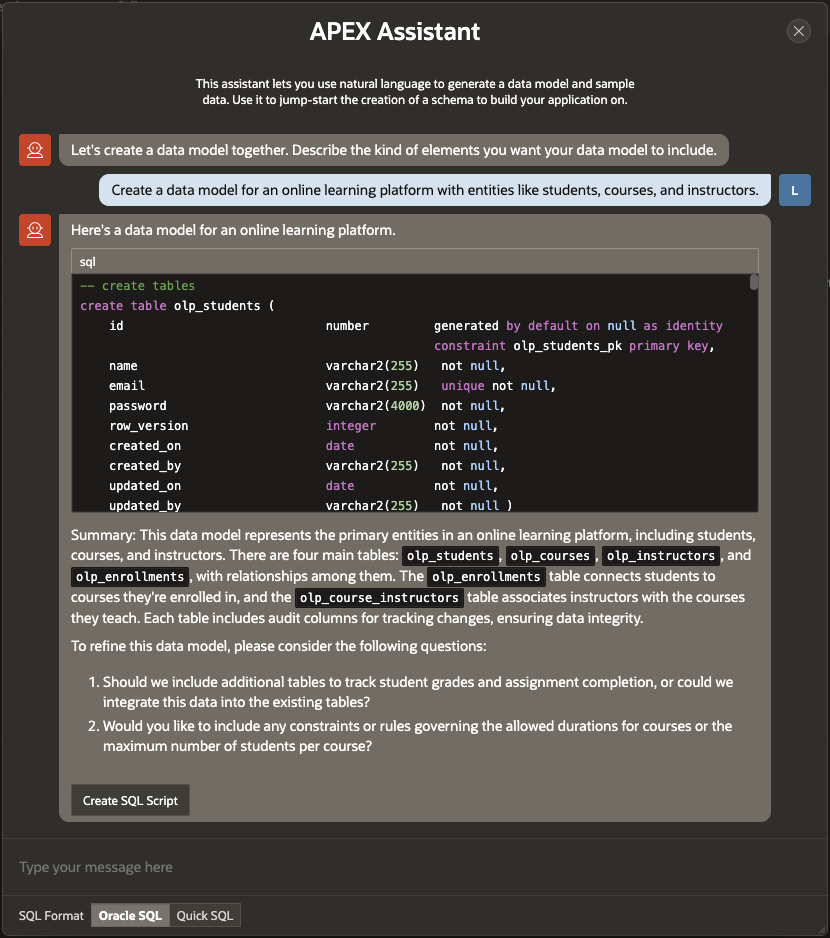
Enhancing the data model is easy—simply provide additional prompts in a conversational manner. For example:
“Include tables to handle assessments (quizzes, exams, projects) and student grades.”
The APEX Assistant incorporates these requirements and updates the data model accordingly.
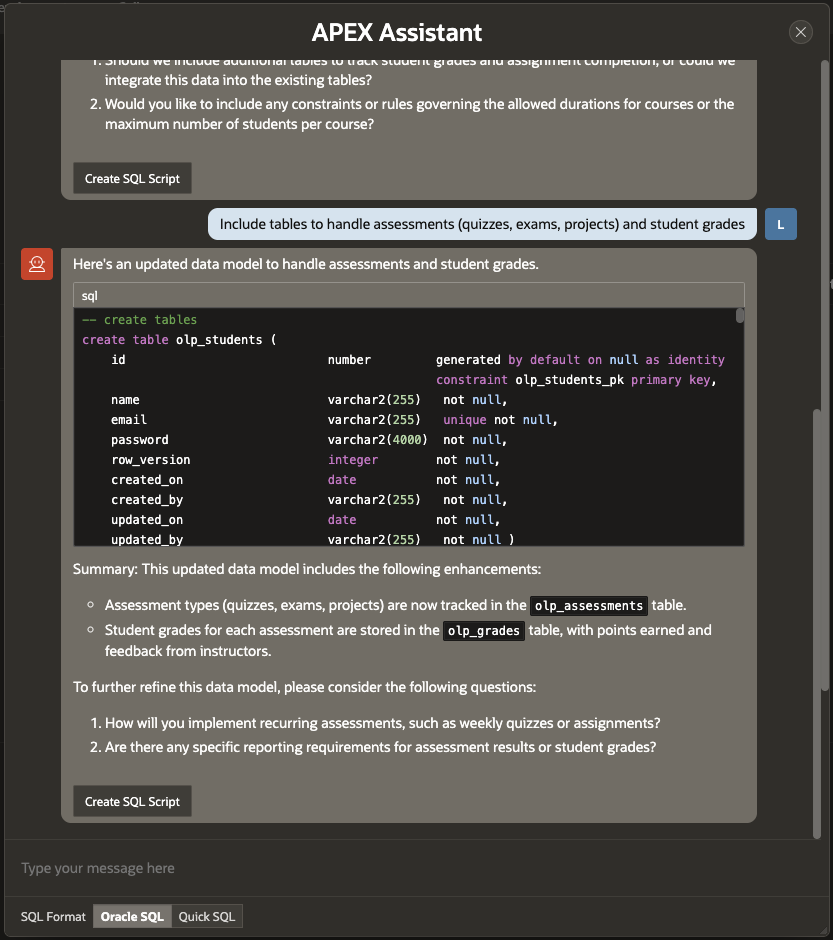
Once satisfied, click Create SQL Script to review the generated script and save it for later use.
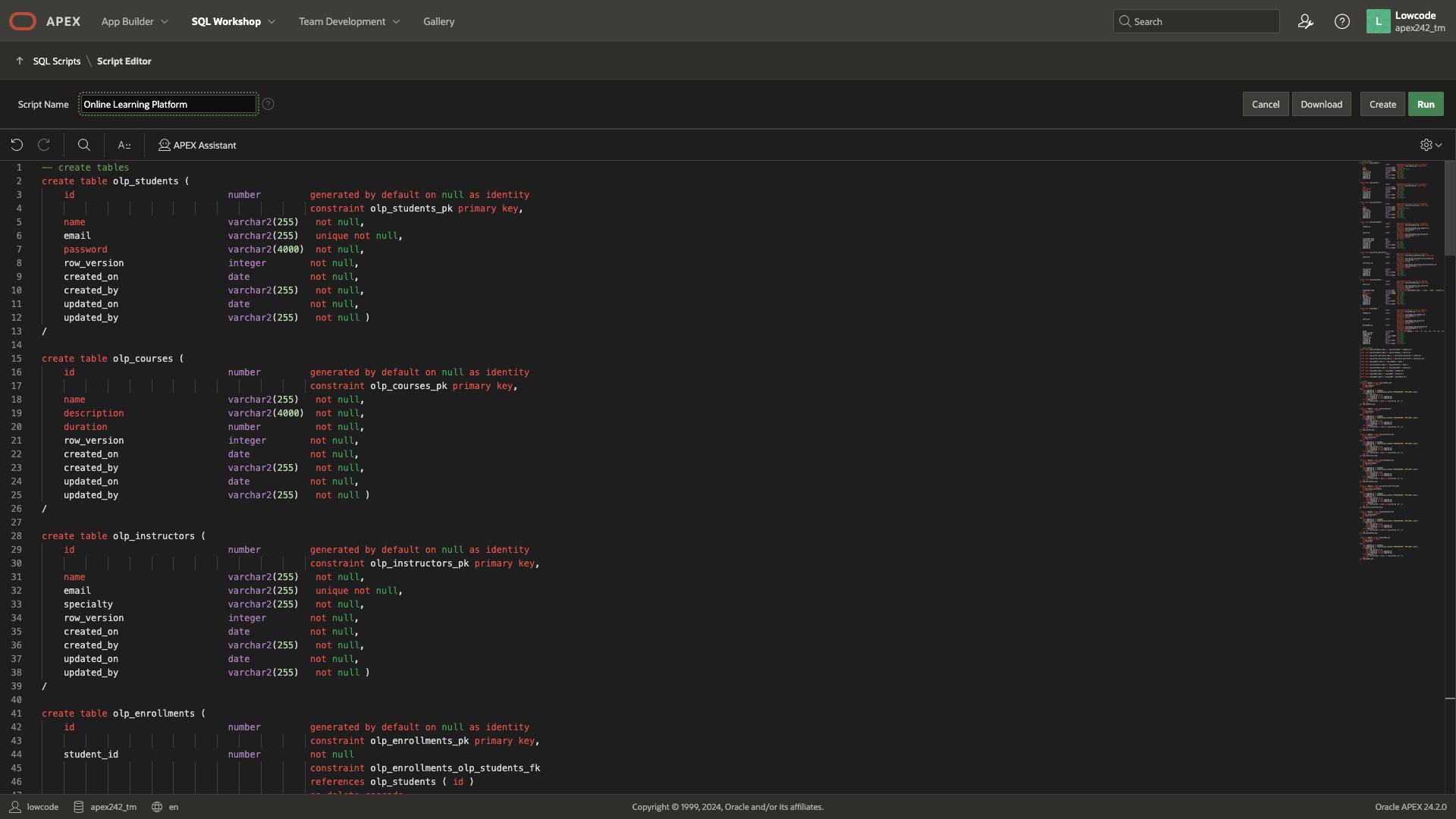
Review the Generated SQL Script
Let’s take a moment to break down and review the generated SQL Script.
Caution: AI-generated code may contain errors or security risks. Oracle recommends you always review and validate all code before use.
The script creates seven tables: olp_students, olp_courses, olp_instructors, olp_enrollments, olp_course_instructors, olp_assessments, and olp_grades. It includes the necessary DDL statements for these tables, along with primary keys and foreign keys to establish relationships between them.
-- create tables
create table olp_students (
id number generated by default on null as identity
constraint olp_students_pk primary key,
student_id varchar2(255) not null,
name varchar2(255) not null,
email varchar2(255) not null unique,
password varchar2(255) not null,
created_on date not null,
created_by varchar2(255) not null,
updated_on date not null,
updated_by varchar2(255) not null,
row_version integer not null
)
/
create table olp_courses (
id number generated by default on null as identity
constraint olp_courses_pk primary key,
course_id varchar2(255) not null unique,
title varchar2(255) not null,
description varchar2(4000),
created_on date not null,
created_by varchar2(255) not null,
updated_on date not null,
updated_by varchar2(255) not null,
row_version integer not null
)
/
create table olp_instructors (
id number generated by default on null as identity
constraint olp_instructors_pk primary key,
instructor_id varchar2(255) not null unique,
name varchar2(255) not null,
email varchar2(255) not null unique,
created_on date not null,
created_by varchar2(255) not null,
updated_on date not null,
updated_by varchar2(255) not null,
row_version integer not null
)
/
create table olp_enrollments (
id number generated by default on null as identity
constraint olp_enrollments_pk primary key,
student_id number not null
constraint olp_enrollments_students_fk
references olp_students ( id ) on delete cascade,
course_id number not null
constraint olp_enrollments_courses_fk
references olp_courses ( id ) on delete cascade,
enrollment_date date not null,
created_on date not null,
created_by varchar2(255) not null,
updated_on date not null,
updated_by varchar2(255) not null,
row_version integer not null
)
/
It also creates the necessary indexes.
-- table index create index olp_students_indx_1 on olp_students ( email ) / create index olp_students_indx_2 on olp_students ( student_id ) / create index olp_courses_indx_1 on olp_courses ( course_id ) / create index olp_instructors_indx_1 on olp_instructors ( email ) / create index olp_instructors_indx_2 on olp_instructors ( instructor_id ) / create index olp_enrollments_indx_1 on olp_enrollments ( student_id ) / create index olp_enrollments_indx_2 on olp_enrollments ( course_id ) /
Additionally, the script generates DDL for triggers that populate the audit columns. It accounts for the possibility that the model might be operating within an APEX session, and thus it populates the update_by column by fetching the APP_USER value from the session using sys_context('APEX$SESSION', 'APP_USER').
-- triggers
create or replace trigger olp_students_biu
before insert or update
on olp_students
for each row
begin
:new.updated_on := sysdate;
:new.updated_by := coalesce(sys_context('APEX$SESSION','APP_USER'),user);
if inserting then
:new.row_version := 1;
:new.created_on := :new.updated_on;
:new.created_by := :new.updated_by;
elsif updating then
:new.row_version := nvl(:old.row_version, 0) + 1;
end if;
end olp_students_biu;
/
create or replace trigger olp_courses_biu
before insert or update
on olp_courses
for each row
begin
:new.updated_on := sysdate;
:new.updated_by := coalesce(sys_context('APEX$SESSION','APP_USER'),user);
if inserting then
:new.row_version := 1;
:new.created_on := :new.updated_on;
:new.created_by := :new.updated_by;
elsif updating then
:new.row_version := nvl(:old.row_version, 0) + 1;
end if;
end olp_courses_biu;
/
create or replace trigger olp_instructors_biu
before insert or update
on olp_instructors
for each row
begin
:new.updated_on := sysdate;
:new.updated_by := coalesce(sys_context('APEX$SESSION','APP_USER'),user);
if inserting then
:new.row_version := 1;
:new.created_on := :new.updated_on;
:new.created_by := :new.updated_by;
elsif updating then
:new.row_version := nvl(:old.row_version, 0) + 1;
end if;
end olp_instructors_biu;
/
create or replace trigger olp_enrollments_biu
before insert or update
on olp_enrollments
for each row
begin
:new.updated_on := sysdate;
:new.updated_by := coalesce(sys_context('APEX$SESSION','APP_USER'),user);
if inserting then
:new.row_version := 1;
:new.created_on := :new.updated_on;
:new.created_by := :new.updated_by;
elsif updating then
:new.row_version := nvl(:old.row_version, 0) + 1;
end if;
end olp_enrollments_biu;
/
create or replace trigger olp_course_instructors_biu
before insert or update
on olp_course_instructors
for each row
begin
:new.updated_on := sysdate;
:new.updated_by := coalesce(sys_context('APEX$SESSION','APP_USER'),user);
if inserting then
:new.row_version := 1;
:new.created_on := :new.updated_on;
:new.created_by := :new.updated_by;
elsif updating then
:new.row_version := nvl(:old.row_version, 0) + 1;
end if;
end olp_course_instructors_biu;
/
create or replace trigger olp_assessments_biu
before insert or update
on olp_assessments
for each row
begin
:new.updated_on := sysdate;
:new.updated_by := coalesce(sys_context('APEX$SESSION','APP_USER'),user);
if inserting then
:new.row_version := 1;
:new.created_on := :new.updated_on;
:new.created_by := :new.updated_by;
elsif updating then
:new.row_version := nvl(:old.row_version, 0) + 1;
end if;
end olp_assessments_biu;
/
create or replace trigger olp_grades_biu
before insert or update
on olp_grades
for each row
begin
:new.updated_on := sysdate;
:new.updated_by := coalesce(sys_context('APEX$SESSION','APP_USER'),user);
if inserting then
:new.row_version := 1;
:new.created_on := :new.updated_on;
:new.created_by := :new.updated_by;
elsif updating then
:new.row_version := nvl(:old.row_version, 0) + 1;
end if;
end olp_grades_biu;
/
Generate Realistic Sample Data for Your Data Model
The APEX Assistant within this feature allows you to effortlessly generate sample data to populate the tables in your data model. This data closely resembles real-world information, assisting in prototyping and testing your data model.
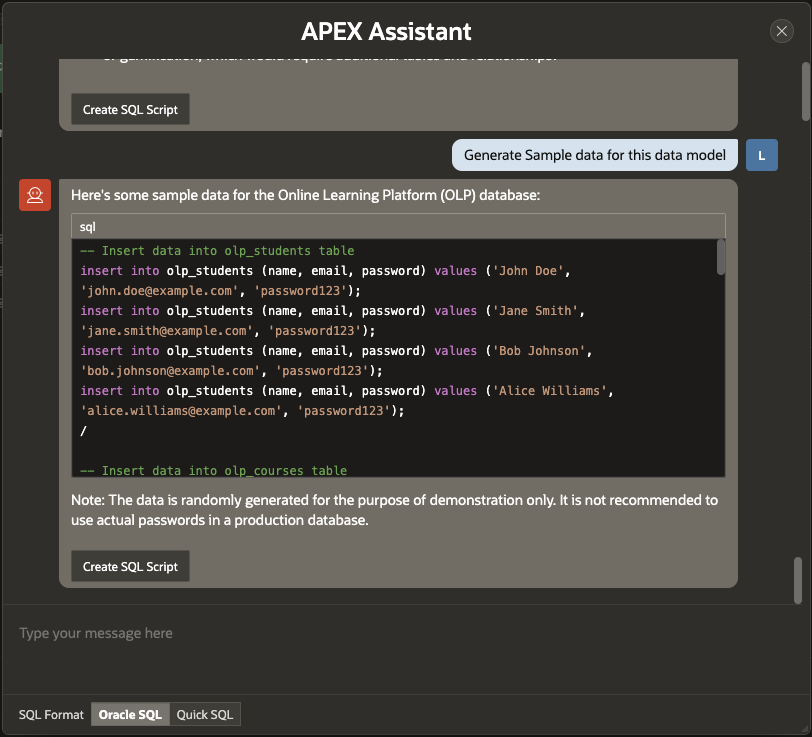
If you need a specific number of rows, you can specify the required amount in the prompt.
Generate Data Model in Quick SQL Format
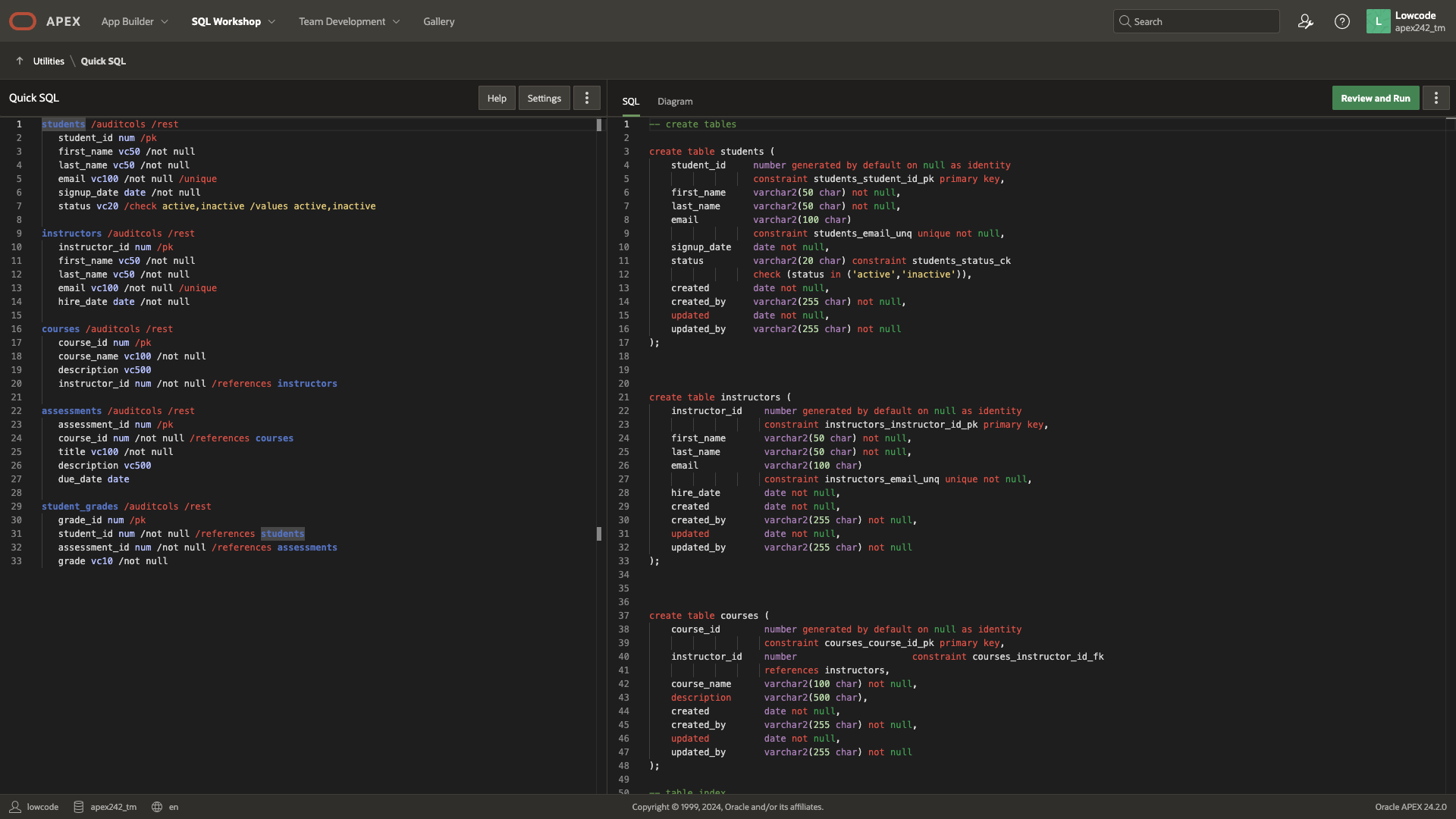
If you’re familiar with Quick SQL shorthand syntax, you can choose to generate the DDL in Quick SQL format. One advantage of this format is its compact and concise structure, which may result in fewer AI tokens being consumed compared to Oracle SQL.
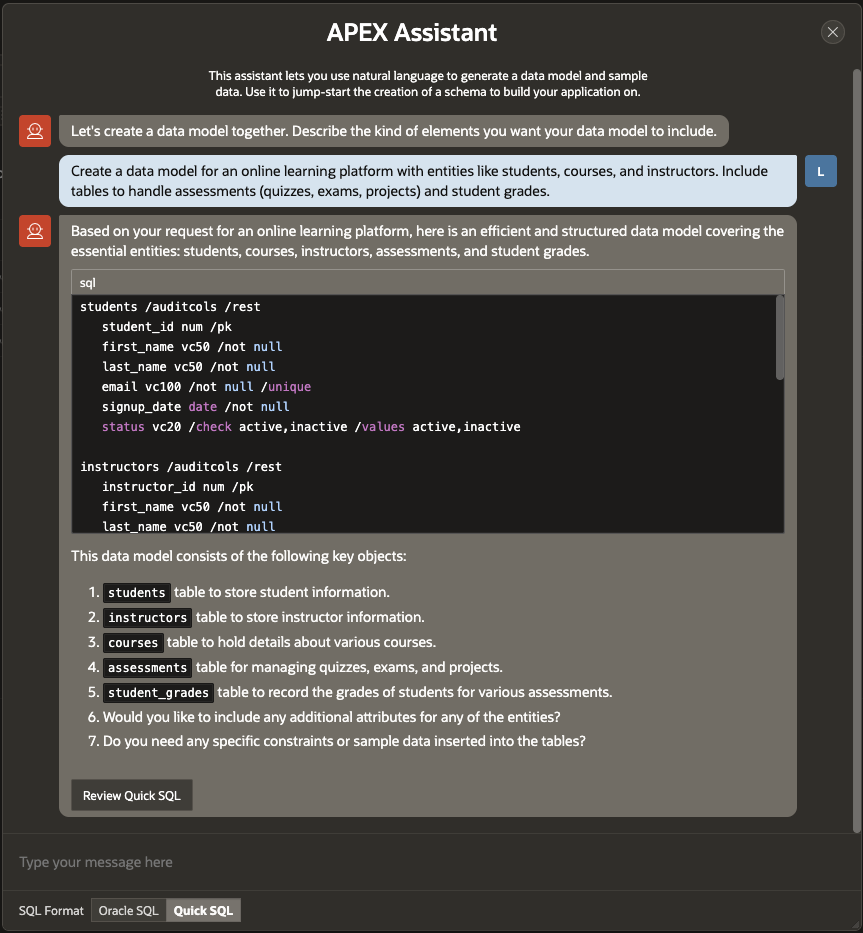
You can click Review Quick SQL button to review the Quick SQL Script generated, along with the converted Oracle SQL as well as the ERD Diagram (under the Diagram Tab)
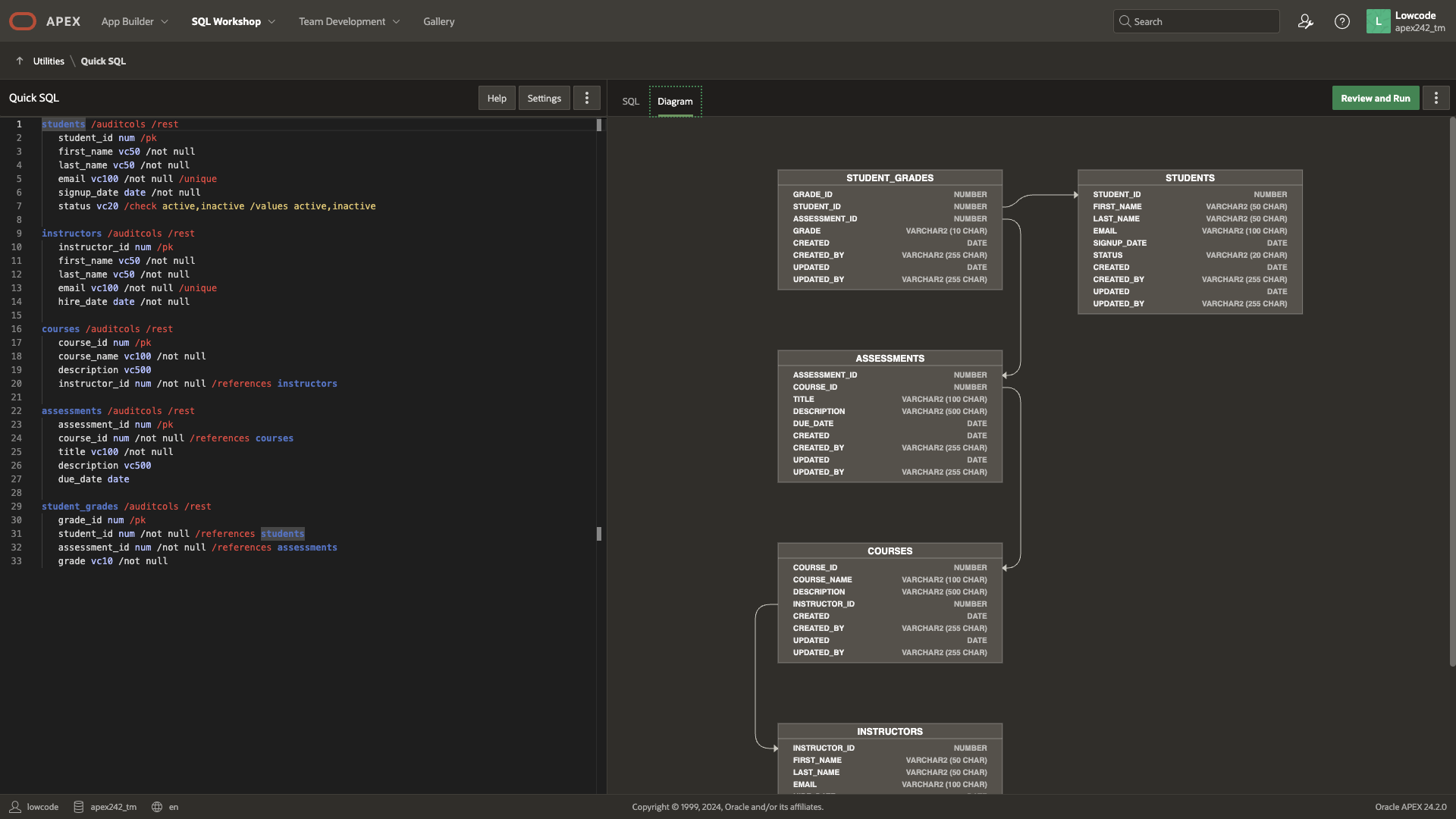
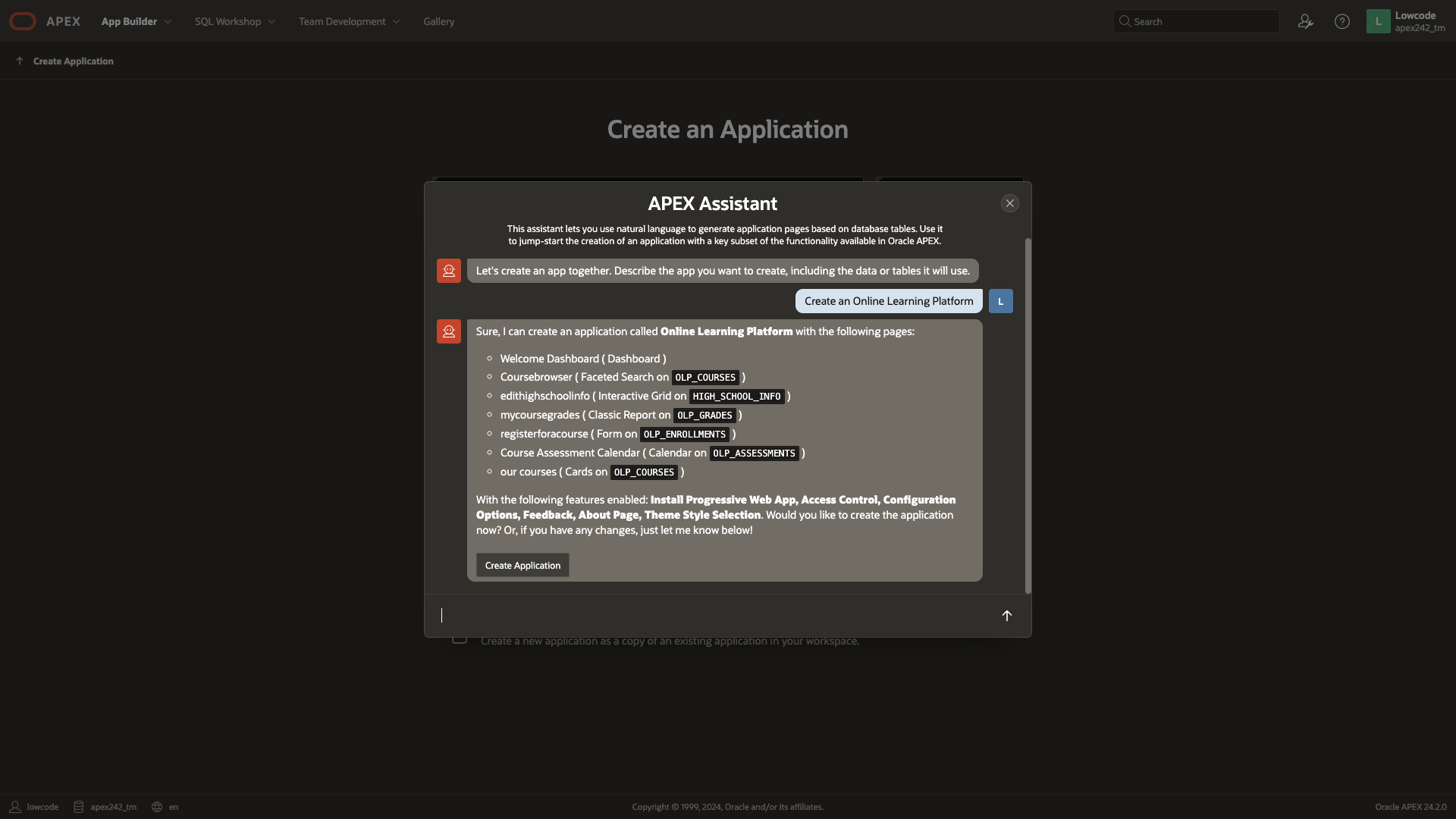
Next Steps: Create an Application on top of the Data Model
With the data model designed and ready, you can now proceed to generate APEX applications based on this AI-generated data model. For instance, you can use the Creating an App Using Generative AI feature to create an application blueprint for the Online Learning Platform. The APEX Assistant examines the available tables in the schema (including the newly generated ones) and incorporates reports, forms, and dashboard pages into the blueprint accordingly.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we looked at how Oracle APEX 24.2’s new Create Data Model Using AI feature can help simplify the often complex and time-consuming process of database schema design. By leveraging the power of Generative AI, developers can now create efficient, scalable, and well-structured data models based on high-level application requirements. This feature not only helps streamline schema creation but also generates synthetic data, enabling testing and prototyping.
Whether you’re building a simple application or laying the foundation for a complex platform like an online learning system, this AI-driven approach offers a significant reduction in manual effort, allowing developers to focus on higher-value tasks. As AI continues to reshape development practices, embracing tools like this can greatly enhance productivity and ensure your applications are built on solid, future-proof foundations.
With this new feature at your disposal, designing efficient data models for your APEX applications has never been easier.
