This blog was originally published on 03 August, 2018
Uploading XLSX files is a very common requirement these days. Application Express at this time only supports uploading CSV files out of the box. The community provides quite a few blog postings and also plug-ins; most of these store the data into a collection, which makes it hard to parse an XLSX outside of an APEX context, e.g. in the background using a scheduler job.
This blog posting shows a method to parse XLSX files with only SQL and PL/SQL. The actual work will be done by a table function, thus no collections and no APEX session is required. Since a table function returns rows and columns, one can easily insert the results into a table, apply some transformation logic, push it into the background with a scheduler job or just display.
The XLSX format is based on XML: an XSLX file is actually a ZIP file (you can easily verify that by renaming to .zip and opening it) containing several XML files. To parse the data, we first have to extract the contents, look up the right XML files and parse these. For the latter task, the XMLTABLE SQL function comes in very handy.
The following example code creates an XLSX_PARSER package. It uses the APEX_ZIP package to unpack the XLSX file and the XMLTABLE SQL function in order to parse the XML. The PARSE function is implemented as a table function which returns the first 50 columns (“A” to “AX”). If you need more columns, you can easily extend the code accordingly; the upper limit is 1000 columns.
create or replace package xlsx_parser is
c_date_format constant varchar2(255) := 'YYYY-MM-DD';
-- we currently support 50 columns - but this can easily be increased. Just increase the columns in the
-- record definition and add corresponing lines into the package body
type xlsx_row_t is record(
line# number,
col01 varchar2(4000), col02 varchar2(4000), col03 varchar2(4000), col04 varchar2(4000), col05 varchar2(4000),
col06 varchar2(4000), col07 varchar2(4000), col08 varchar2(4000), col09 varchar2(4000), col10 varchar2(4000),
col11 varchar2(4000), col12 varchar2(4000), col13 varchar2(4000), col14 varchar2(4000), col15 varchar2(4000),
col16 varchar2(4000), col17 varchar2(4000), col18 varchar2(4000), col19 varchar2(4000), col20 varchar2(4000),
col21 varchar2(4000), col22 varchar2(4000), col23 varchar2(4000), col24 varchar2(4000), col25 varchar2(4000),
col26 varchar2(4000), col27 varchar2(4000), col28 varchar2(4000), col29 varchar2(4000), col30 varchar2(4000),
col31 varchar2(4000), col32 varchar2(4000), col33 varchar2(4000), col34 varchar2(4000), col35 varchar2(4000),
col36 varchar2(4000), col37 varchar2(4000), col38 varchar2(4000), col39 varchar2(4000), col40 varchar2(4000),
col41 varchar2(4000), col42 varchar2(4000), col43 varchar2(4000), col44 varchar2(4000), col45 varchar2(4000),
col46 varchar2(4000), col47 varchar2(4000), col48 varchar2(4000), col49 varchar2(4000), col50 varchar2(4000));
type xlsx_tab_t is table of xlsx_row_t;
--==================================================================================================================
-- table function parses the XLSX file and returns the first 15 columns.
-- pass either the XLSX blob directly or reference a name in the APEX_APPLICATION_TEMP_FILES table.
--
-- p_xlsx_name - NAME column of the APEX_APPLICATION_TEMP_FILES table
-- p_xlsx_content - XLSX as a BLOB
-- p_worksheet_name - Worksheet to extract
--
-- usage:
--
-- select * from table(
-- xlsx_parser.parse(
-- p_xlsx_name => :P1_XLSX_FILE,
-- p_worksheet_name => :P1_WORKSHEET_NAME ) );
--
function parse(
p_xlsx_name in varchar2 default null,
p_xlsx_content in blob default null,
p_worksheet_name in varchar2 default 'sheet1',
p_max_rows in number default 1000000 ) return xlsx_tab_t pipelined;
--==================================================================================================================
-- table function to list the available worksheets in an XLSX file
--
-- p_xlsx_name - NAME column of the APEX_APPLICATION_TEMP_FILES table
-- p_xlsx_content - XLSX as a BLOB
--
-- usage:
--
-- select * from table(
-- xlsx_parser.get_worksheets(
-- p_xlsx_name => :P1_XLSX_FILE ) );
--
function get_worksheets(
p_xlsx_content in blob default null,
p_xlsx_name in varchar2 default null ) return apex_t_varchar2 pipelined;
--==================================================================================================================
-- date and datetimes are stored as a number in XLSX; this function converts that number to an ORACLE DATE
--
-- p_xlsx_date_number numeric XLSX date value
--
-- usage:
-- select xlsx_parser.get_date( 46172 ) from dual;
--
function get_date( p_xlsx_date_number in number ) return date;
end xlsx_parser;
/
sho err
create or replace package body xlsx_parser is
g_worksheets_path_prefix constant varchar2(14) := 'xl/worksheets/';
--==================================================================================================================
function get_date( p_xlsx_date_number in number ) return date is
begin
return
case when p_xlsx_date_number > 61
then DATE'1900-01-01' - 2 + p_xlsx_date_number
else DATE'1900-01-01' - 1 + p_xlsx_date_number
end;
end get_date;
--==================================================================================================================
procedure get_blob_content(
p_xlsx_name in varchar2,
p_xlsx_content in out nocopy blob )
is
begin
if p_xlsx_name is not null then
select blob_content into p_xlsx_content
from apex_application_temp_files
where name = p_xlsx_name;
end if;
exception
when no_data_found then
null;
end get_blob_content;
--==================================================================================================================
function extract_worksheet(
p_xlsx in blob,
p_worksheet_name in varchar2 ) return blob
is
l_worksheet blob;
begin
if p_xlsx is null or p_worksheet_name is null then
return null;
end if;
l_worksheet := apex_zip.get_file_content(
p_zipped_blob => p_xlsx,
p_file_name => g_worksheets_path_prefix || p_worksheet_name || '.xml' );
if l_worksheet is null then
raise_application_error(-20000, 'WORKSHEET "' || p_worksheet_name || '" DOES NOT EXIST');
end if;
return l_worksheet;
end extract_worksheet;
--==================================================================================================================
procedure extract_shared_strings(
p_xlsx in blob,
p_strings in out nocopy wwv_flow_global.vc_arr2 )
is
l_shared_strings blob;
begin
l_shared_strings := apex_zip.get_file_content(
p_zipped_blob => p_xlsx,
p_file_name => 'xl/sharedStrings.xml' );
if l_shared_strings is null then
return;
end if;
select shared_string
bulk collect into p_strings
from xmltable(
xmlnamespaces( default 'http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/spreadsheetml/2006/main' ),
'//si'
passing xmltype.createxml( l_shared_strings, nls_charset_id('AL32UTF8'), null )
columns
shared_string varchar2(4000) path 't/text()' );
end extract_shared_strings;
--==================================================================================================================
procedure extract_date_styles(
p_xlsx in blob,
p_format_codes in out nocopy wwv_flow_global.vc_arr2 )
is
l_stylesheet blob;
begin
l_stylesheet := apex_zip.get_file_content(
p_zipped_blob => p_xlsx,
p_file_name => 'xl/styles.xml' );
The package provides the following functions:
FUNCTION GET_WORKSHEETS RETURNS APEX_T_VARCHAR2 Argument Name Type In/Out Default? ------------------------------ ----------------------- ------ -------- P_XLSX_CONTENT BLOB IN DEFAULT P_XLSX_NAME VARCHAR2 IN DEFAULT FUNCTION PARSE RETURNS XLSX_TAB_T Argument Name Type In/Out Default? ------------------------------ ----------------------- ------ -------- P_XLSX_NAME VARCHAR2 IN DEFAULT P_XLSX_CONTENT BLOB IN DEFAULT P_WORKSHEET_NAME VARCHAR2 IN DEFAULT P_MAX_ROWS NUMBER IN DEFAULT
You can pass either the XLSX content as a BLOB or the name of an uploaded file. In the latter case, the package will look up the file name in the APEX_APPLICATION_TEMP_FILES table. A typical call sequence is as follows:
- Look up the worksheets contained in the XSLX file with XLSX_PARSER.GET_WORKSHEETS
- Retrieve the Worksheet data with XLSX_PARSER.PARSE.
Let’s try this out. Create an APEX application with an empty page, then add the following elements to that page.
- Add a Region of Static HTML type.
- Add a File Browse item named PX_XLSX_FILE. Choose Table APEX_APPLICATION_TEMP_FILES as the Storage Type and keep the files until the End Of Session.
- Add a Button to Upload the file. Choose Submit Page as the button action.
Your page should now look as follows:
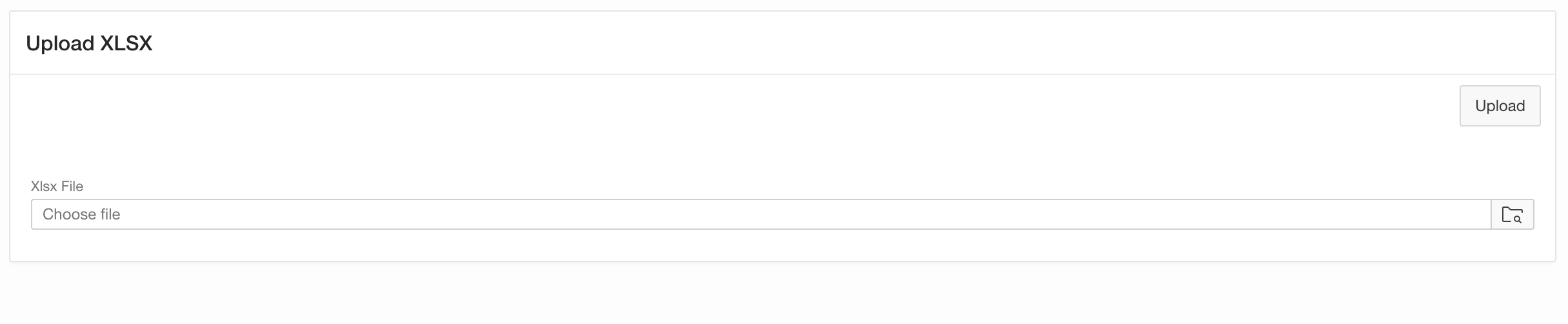 You can already upload a file, but nothing will happen. Next, we’ll want to show a select list to pick one of the worksheets contained in the XLSX file.
You can already upload a file, but nothing will happen. Next, we’ll want to show a select list to pick one of the worksheets contained in the XLSX file.
- Add a Select List item named PX_WORKSHEET.
- Use SQL Query as the List Of Values Type and provide the following SQL query:
select column_value d, column_value r from table( xlsx_parser.get_worksheets( p_xlsx_name => :PX_XLSX_FILE ) )
- Set Display Extra Values to No, Display Null Value to Yes and use – Choose – as the Null Display Value.
- Finally add a Server-Side condition to only display the select list when the PX_XLSX_FILE item IS NOT NULL (when a file has actually been uploaded)
Now run your page again. After you have uploaded an XSLX file, your page should look as follows:
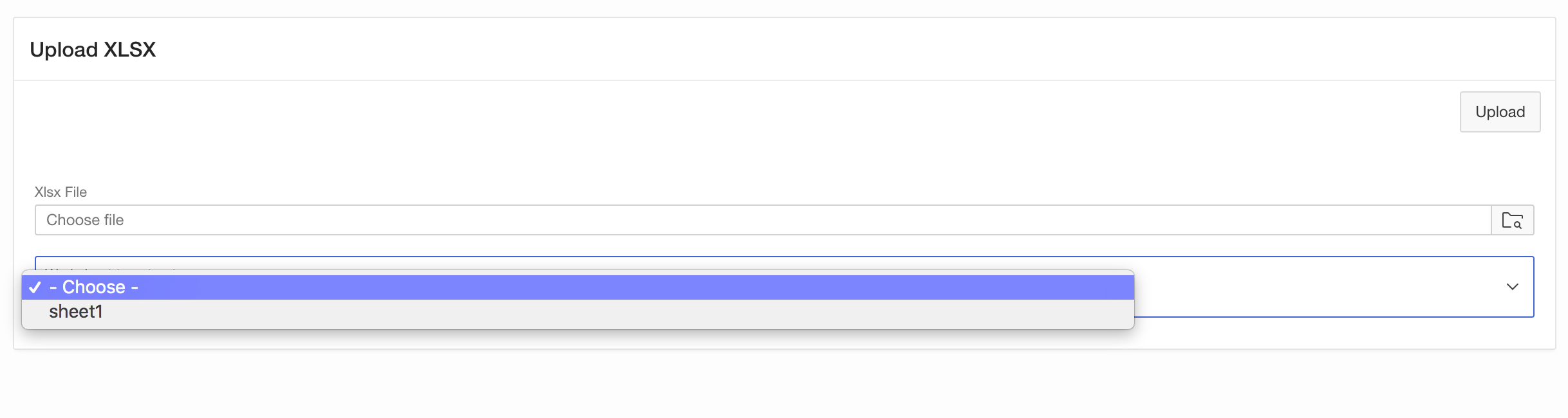
So we can now pick a worksheet. So far, so good. Time to actually do the job and extract data from the XLSX file. For now, we just want to display the data as a classic report. So create a Classic Report region and use the following SQL Query.
select * from table(
xlsx_parser.parse(
p_xlsx_name => :PX_XLSX_FILE,
p_worksheet_name => :PX_WORKSHEET ) );
Add the PX_WORKSHEET item to the Classic Reports Page Items to Submit attribute. Then add a Dynamic Action in order to refresh the report when a worksheet has been chosen in the Select List item.
- The dynamic action should fire on the Change event of the PX_WORKSHEET item
- As the TRUE action, choose Refresh of the Classic Report region you just have created.
You then should be able to do the following steps:
- Run the page and upload an XLSX file
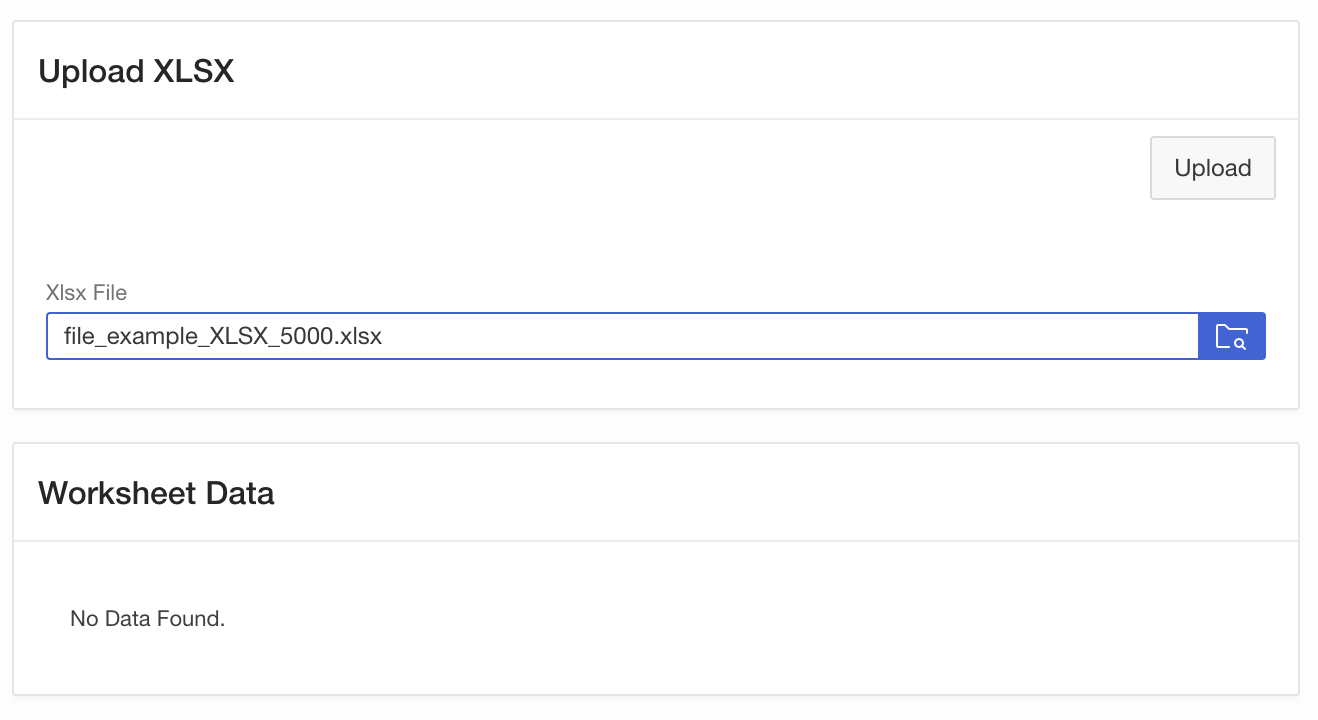
- Pick a worksheet from the select list
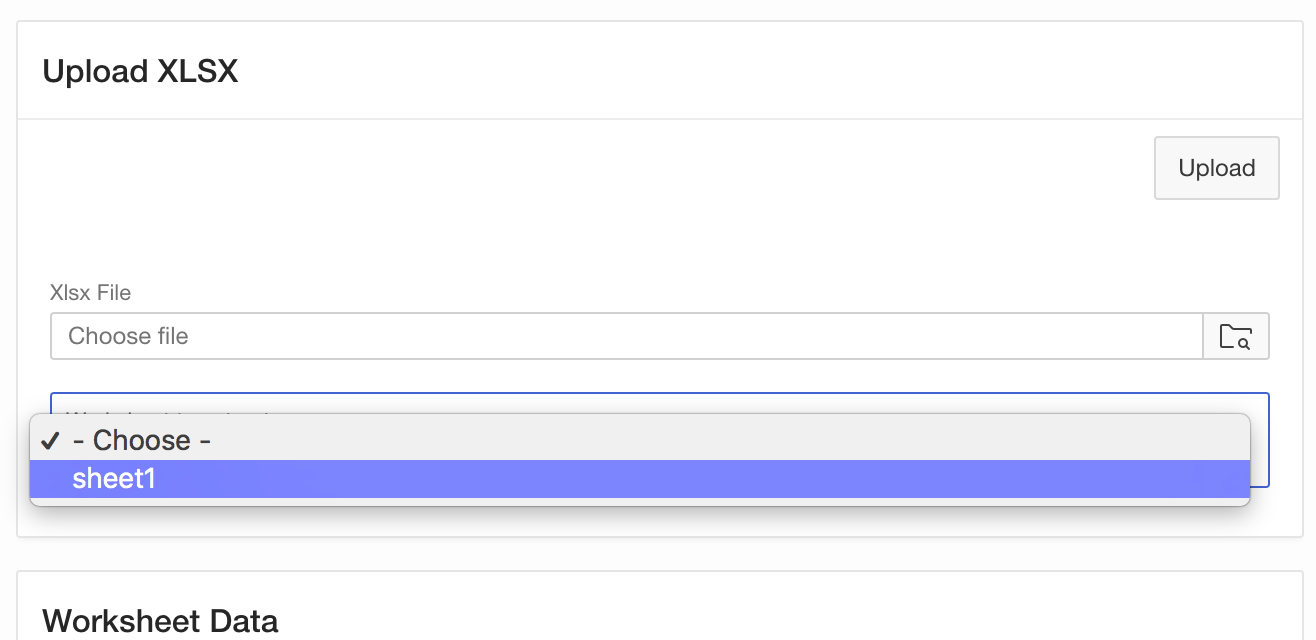
- The Classic Report refreshes and shows the first 50 columns of worksheet data
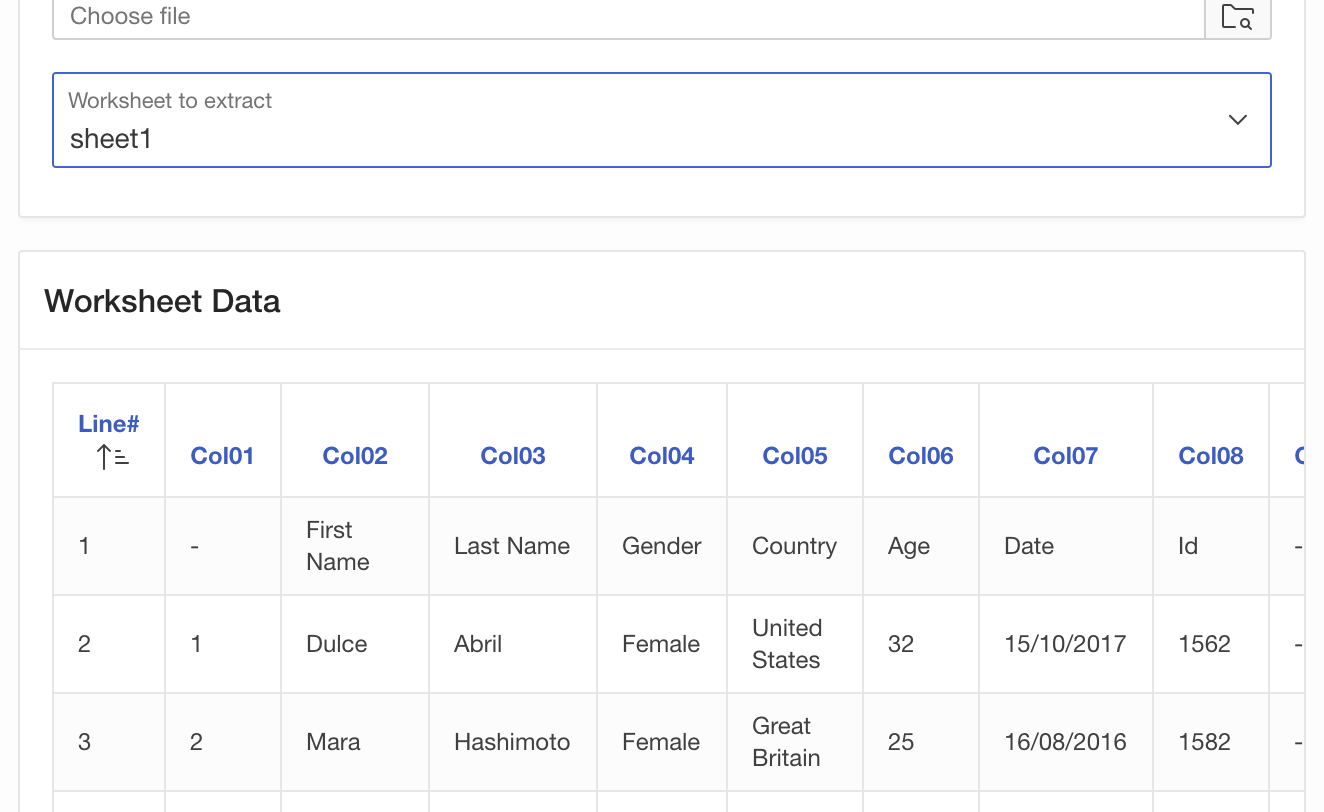
And that’s it … the nice thing is that there are no limits to process the worksheet data …
- You can simply create a table …
create table worksheet_data as select col02 as first_name, col03 as last_name, col05 as country from table( xlsx_parser.parse( p_xlsx_name => :PX_XLSX_FILE, p_worksheet_name => :PX_WORKSHEET ) ); - You can apply a few transformations …
insert into worksheet_data( select cast( col02 as varchar2(200) ) as first_name, cast( col03 as varchar2(200) ) as last_name, case col04 when 'Female' then 'F' when 'Male' then 'M' end as gender, cast( col05 as varchar2(200) ) as country, to_number( to_char( sysdate, 'YYYY') ) - to_number( col06 ) as birth_year from table( xlsx_parser.parse( p_xlsx_name => :PX_XLSX_FILE, p_worksheet_name => :PX_WORKSHEET ) ) where line# != 1) - You can also create a DBMS_SCHEDULER job to push the task into the background. Note that this job does not have access to APEX session state – so you need to store the BLOB into your own table, then.
Try the sample code out – once the table function returns data, there are no limits for further processing any more. You can do with the data whatever you want: from just displaying over loading into a table to executing complex processing in the background: Everything is possible.
