This blog was originally published on Oct 25, 2019.
One of the most exciting new features in APEX 19.2 is Faceted Search. Faceted Search (or faceted navigation) is seen pretty often on the internet; typically on shop or sales web sites. The end user can set filters using Facets on the left or upper side of the screen. A facet shows possible values together with the occurrence count within the result set. After the end user changed a facet, results, dependent facets and occurrence counts refresh immediately.
And you can try that feature out on apex.oracle.com today!
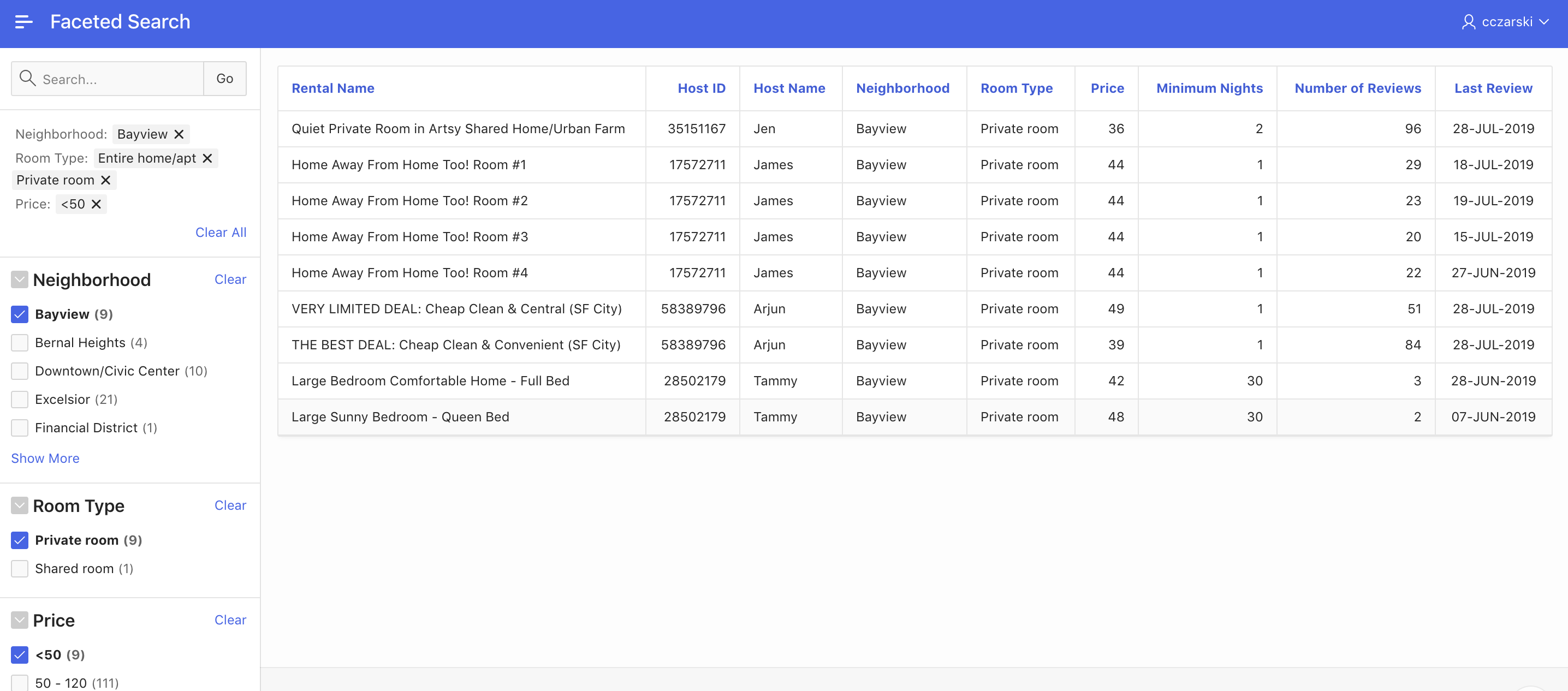
Fig. 1: Faceted Search in APEX 19.2
Create a new Faceted Search page
A faceted search page can be created using the Create Page wizard. Faceted Search is one of the Create Report Page options.
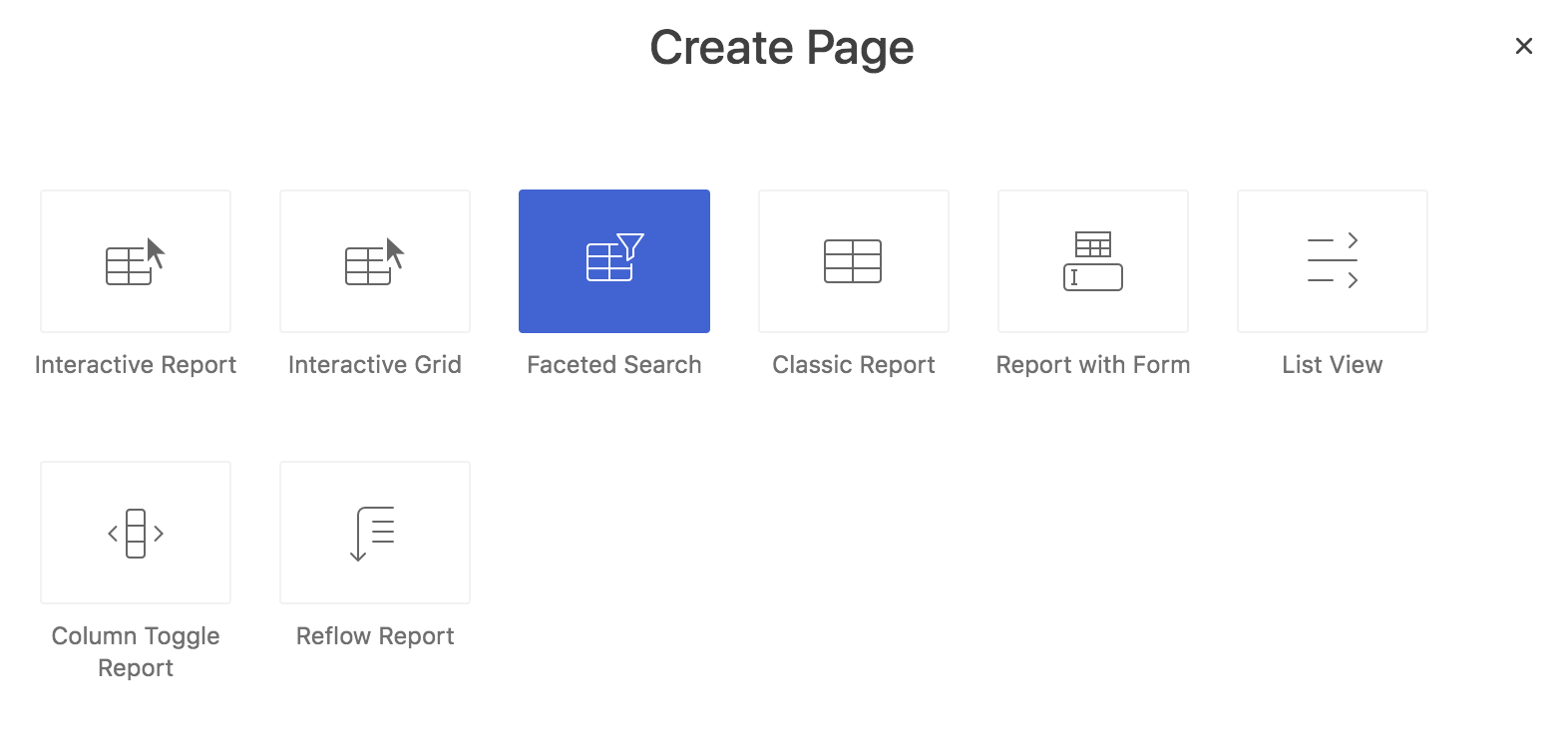
Fig. 2: Faceted Search is an option of the Create Report page wizard
After choosing Faceted Search, and setting the usual attributes, like page name or whether to create a navigation menu entry, the Data Source step appears. Here the developer chooses where the data for the faceted search page should come from.
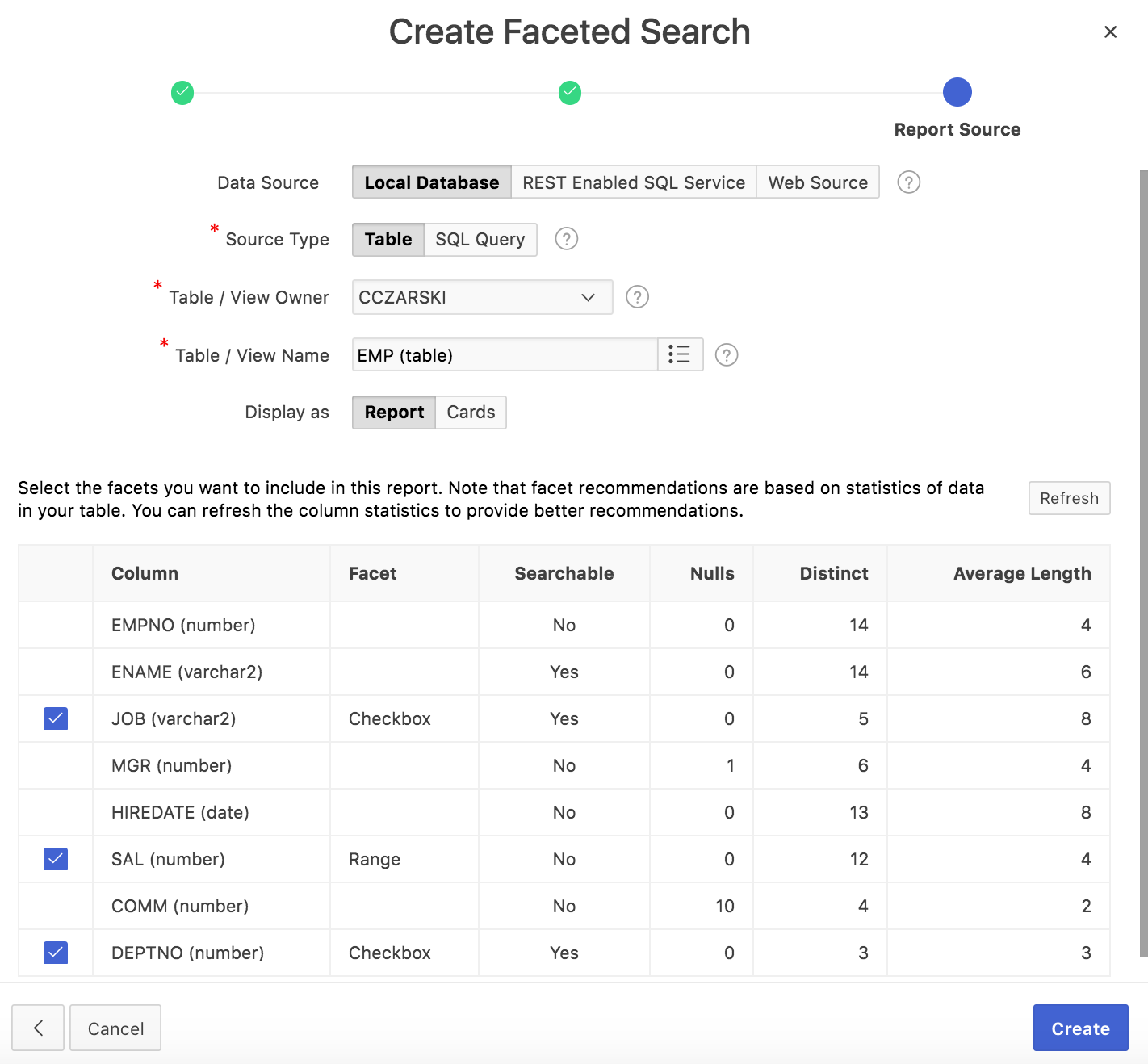
Fig. 3: APEX proposes and creates facets for database columns automatically
Faceted Search pages can be created for tables and SQL queries; for the local database, REST Enabled SQL services and REST services. For local tables, APEX maintains a dictionary cache, containing information about table columns, foreign keys, and actual data,. Based on this cache, APEX can propose appropriate facets and create them automatically, as fig. 3 illustrates.
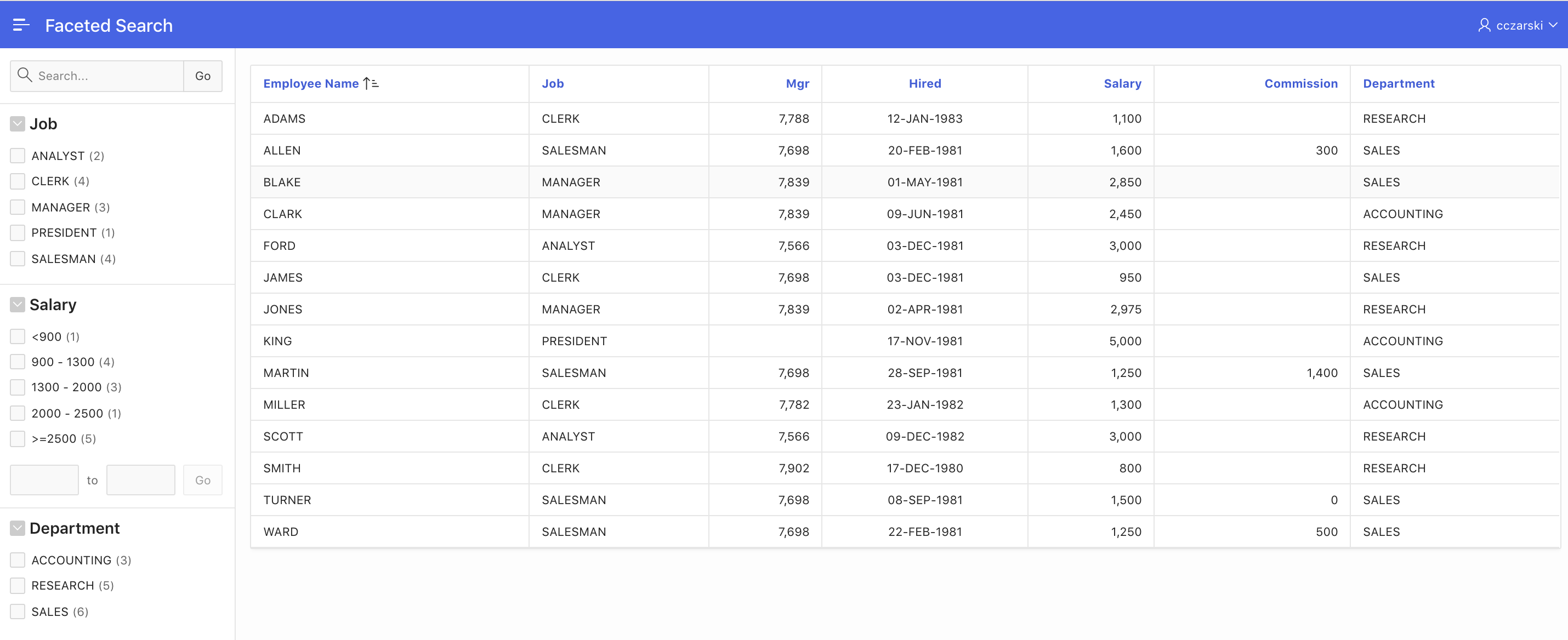
Fig. 4: Generated Faceted Search page for the EMP table.
Fig. 4 shows the generated faceted search page for the EMP table. Based on the dictionary cache, APEX was able to follow the foreign key relationship to the DEPT table, and to create the facet with appropriate display values. Also, the values of the SAL column were distributed to buckets and a range facet was created. All facets show the occurrence count by default; changes to the facets lead to immediate refresh of the result list.
Apply changes to the new Faceted Search page
Let’s now apply some changes to the page we just have generated. After clicking Edit Page on the developer toolbar, Page Designer opens and shows the components of the page.
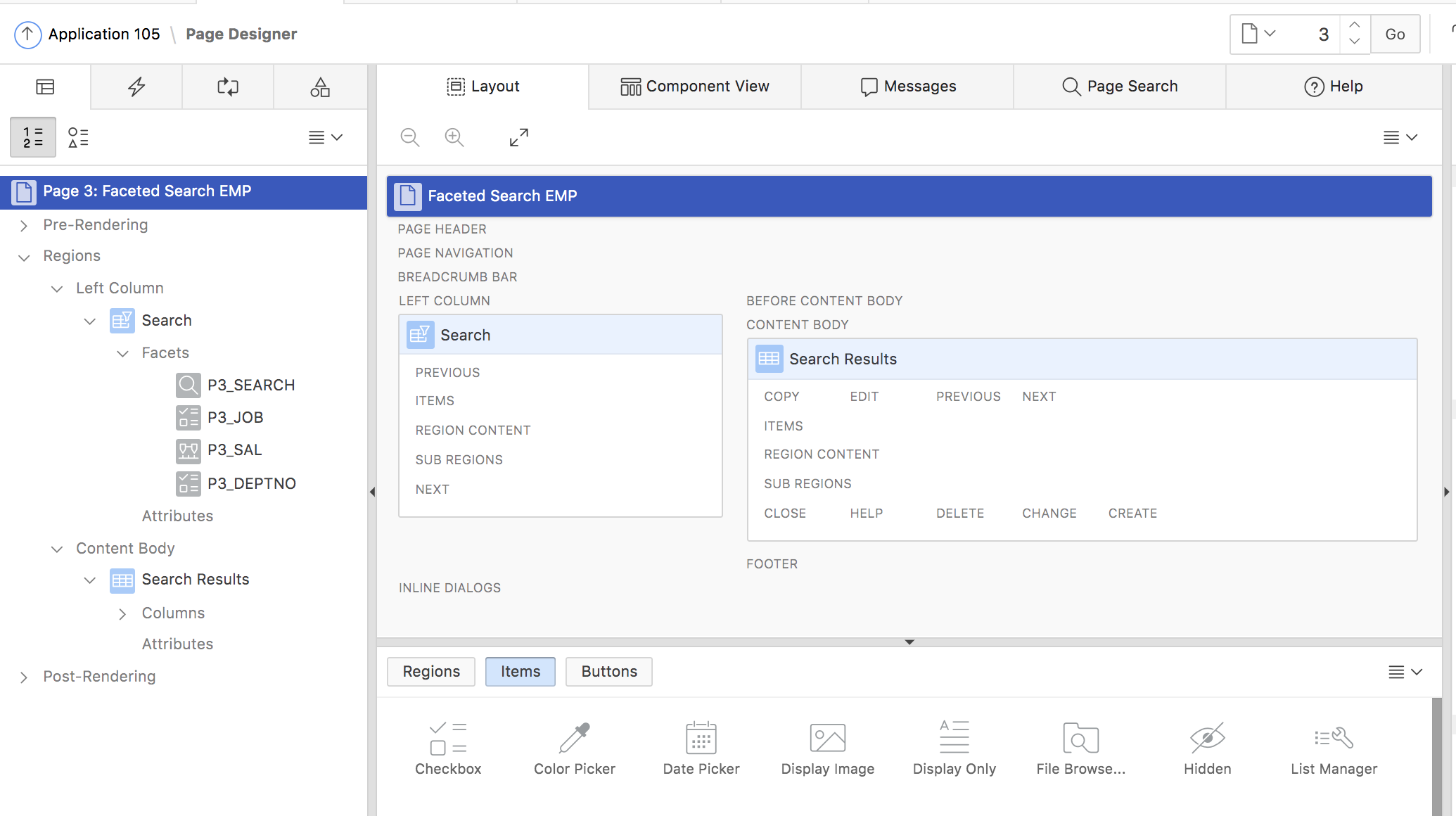
Fig. 5: Faceted Search page in page designer
We can see, that the page consists of a classic report region, showing search results, and a region of the new Faceted Search type, which holds the facets. The Faceted Search region is linked to the Classic Report region (Fig. 6), and each Facet is linked to one of the Classic Report result columns (Fig.7).
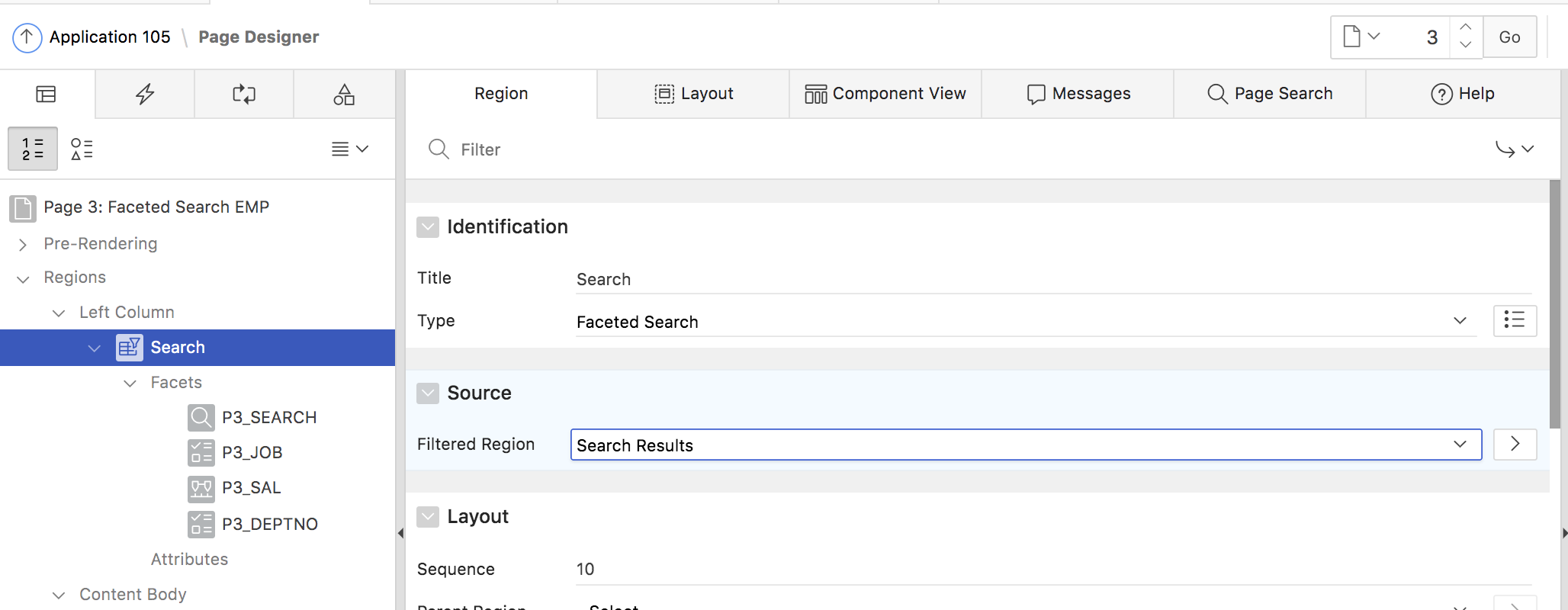
Fig. 6: The Faceted Search region is linked to the Classic Report region.
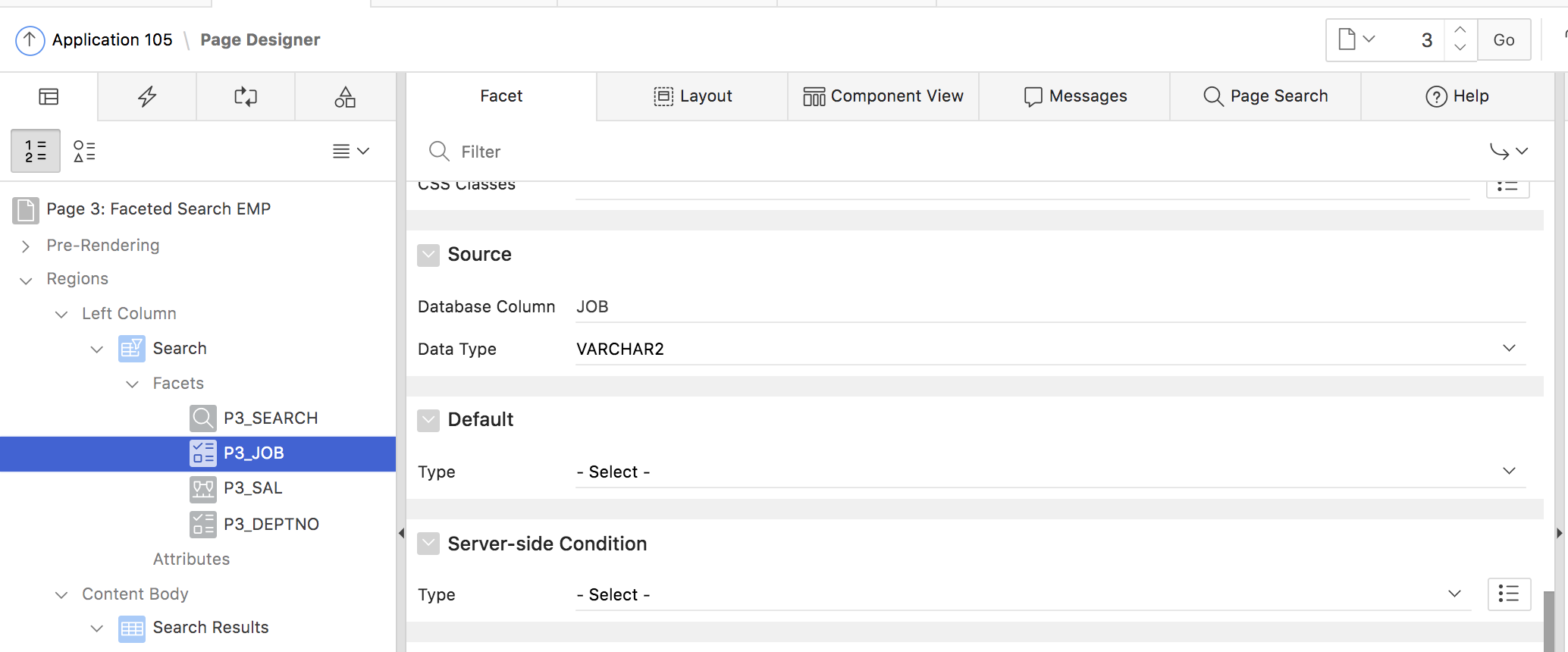
Fig. 7: Each facet is linked to a report column
Facets can display as different UI types. APEX 19.2 provides the following facet types.
- Checkbox
- Radio Group
- Select List
- Range
- Search
The checkbox, select list and radio group facets are rather self-explaining: Checkboxes allow to pick multiple values to used for result filtering, whereas radio groups or select lists only allow to pick one of the values.
It’s obvious that faceted search pages can also be created manually using only Page Designer:
- Create the Classic Report region and provide its data source
- Create the Faceted Search region and link it to the Classic Report region
- Add Facets to the Faceted Search region as needed.
Search Facet
The Search facet allows the end user to perform some text based search on the result list. Only one search facet is supported for a faceted search region. The report columns to use for searching are configured in the Source section within the attributes of the search facet (fig. 8).
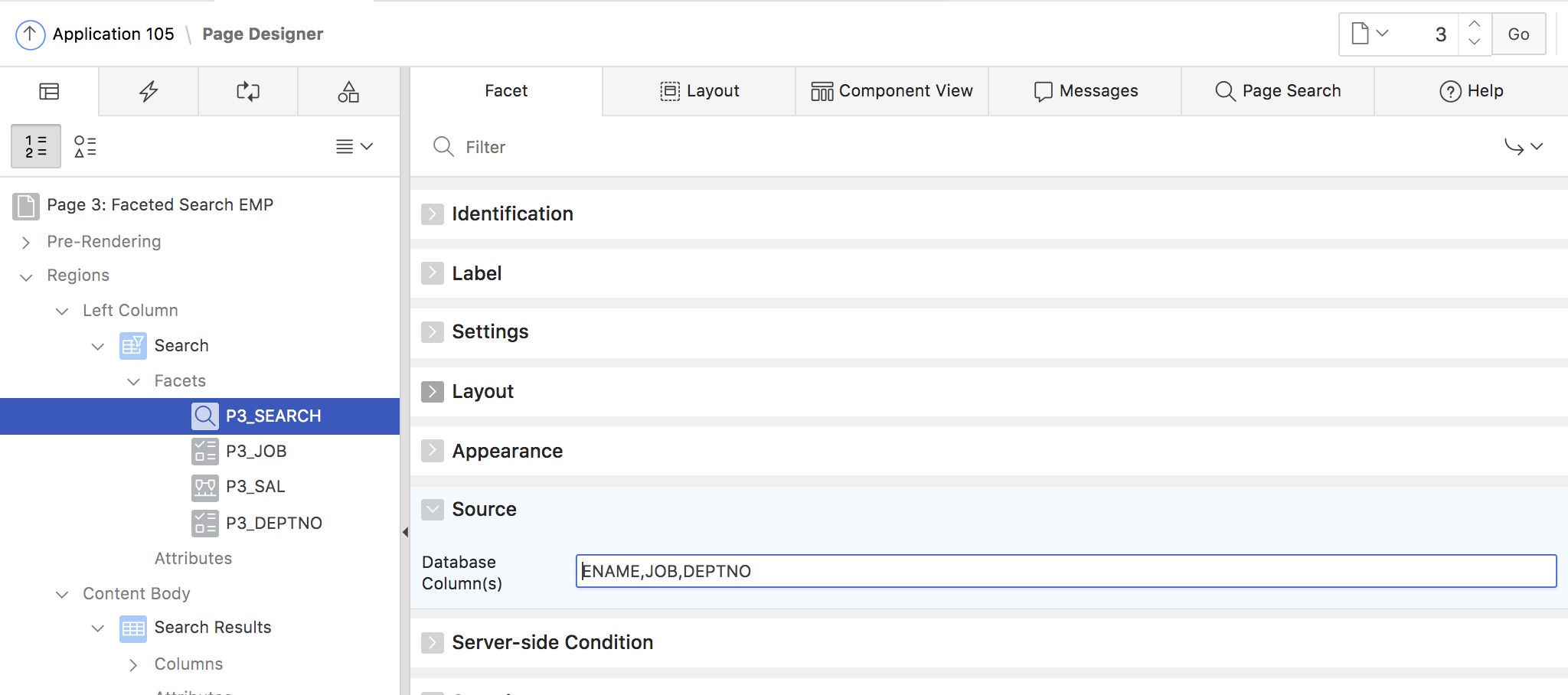
Fig. 8: Configure report columns to use for the Search Facet
If the column, referenced in the search facet, uses an LOV for display, the search facet will automatically search on the LOV display column instead of the return column. The search facet by default appears as the first facet in the facets region. As an alternative, the developer can create a page item of the Text Field type and use that as the search facet (Fig. 9).
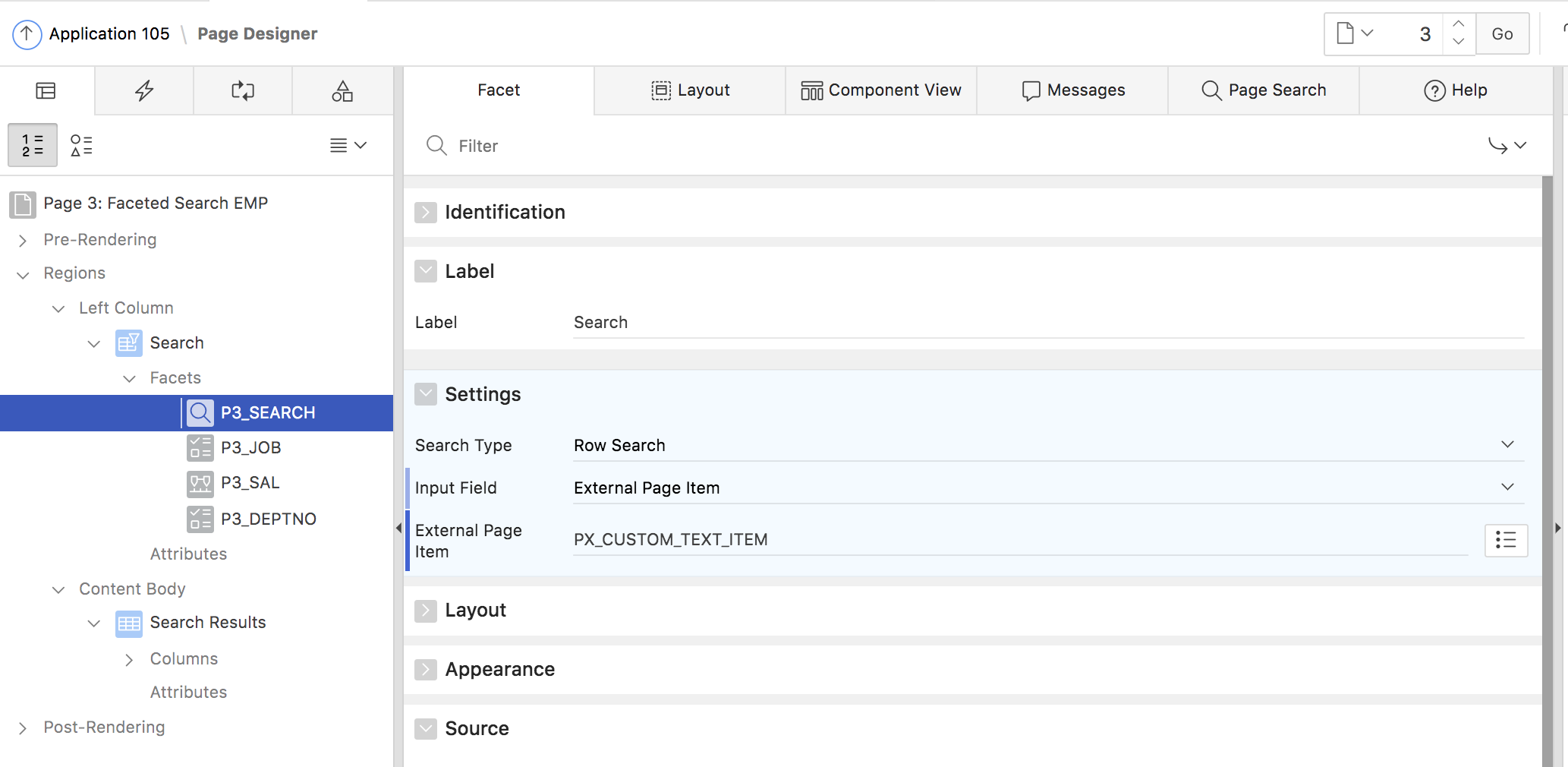
Fig. 9: Configure a custom text item as the search facet
Fig. 10 shows a faceted search page using a custom page item for the search facet.
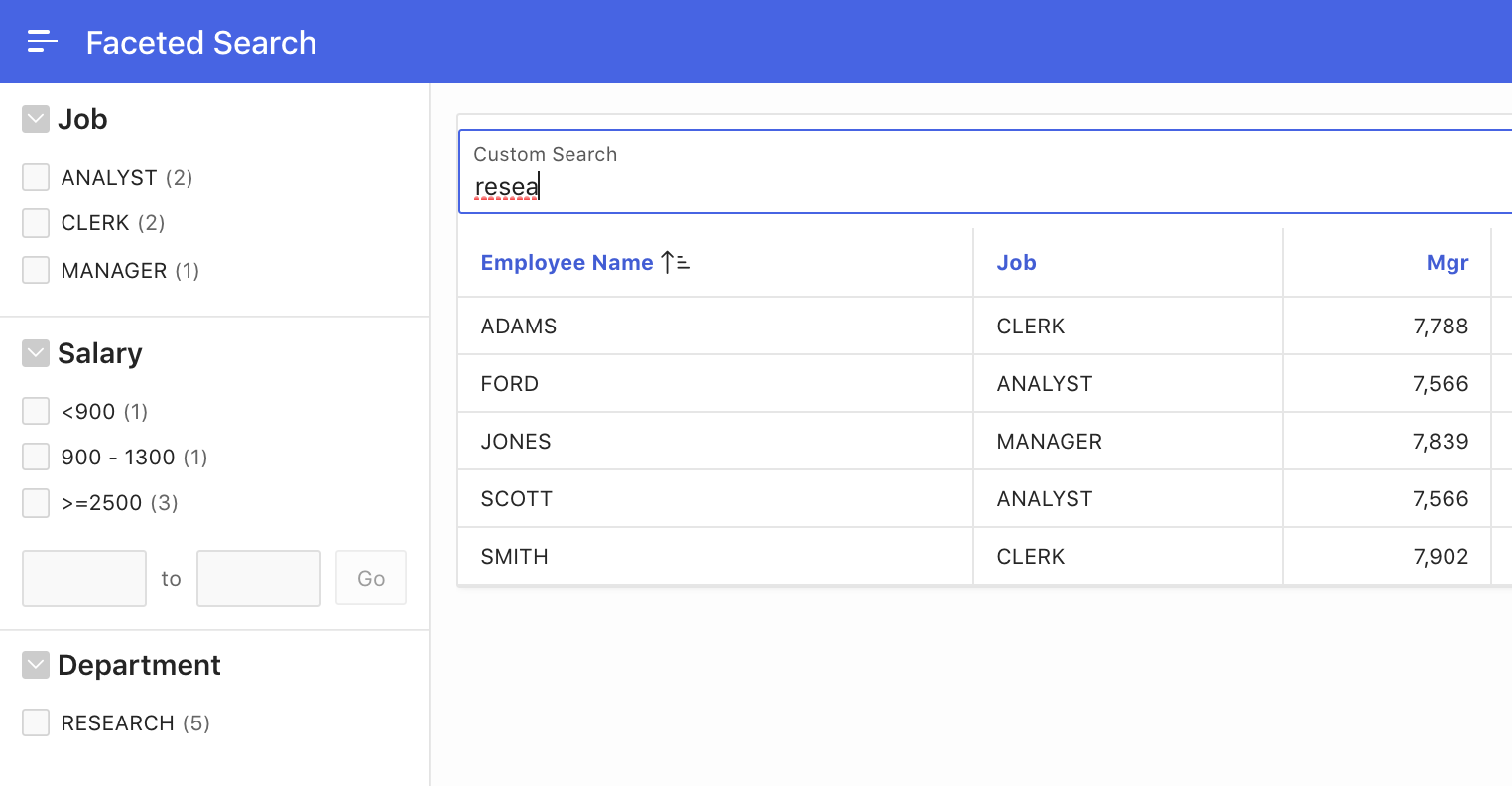
Fig. 10: Usage of an external page item for the Search facet.
If an Oracle Text index exists for the table, the search facet can be configured to use that index for searching, which leverages linguistic or fuzzy features for Faceted Search in APEX.
Range Facet
The Range Facet allows to filter the result list for values between a lower and upper boundary. A range facet consists of an LOV with predefined ranges to pick from, two text fields to manually enter the lower and upper boundary, or both. For the predefined ranges, the normal APEX LOV infrastructure is used: the LOV can thus be a static LOV, defined in Page Designer, or a dynamic one, using a SQL Query. In both cases, the LOV return value needs to use the pipe (|) character, to separate upper and lower values. Fig 11. shows a configuration example.
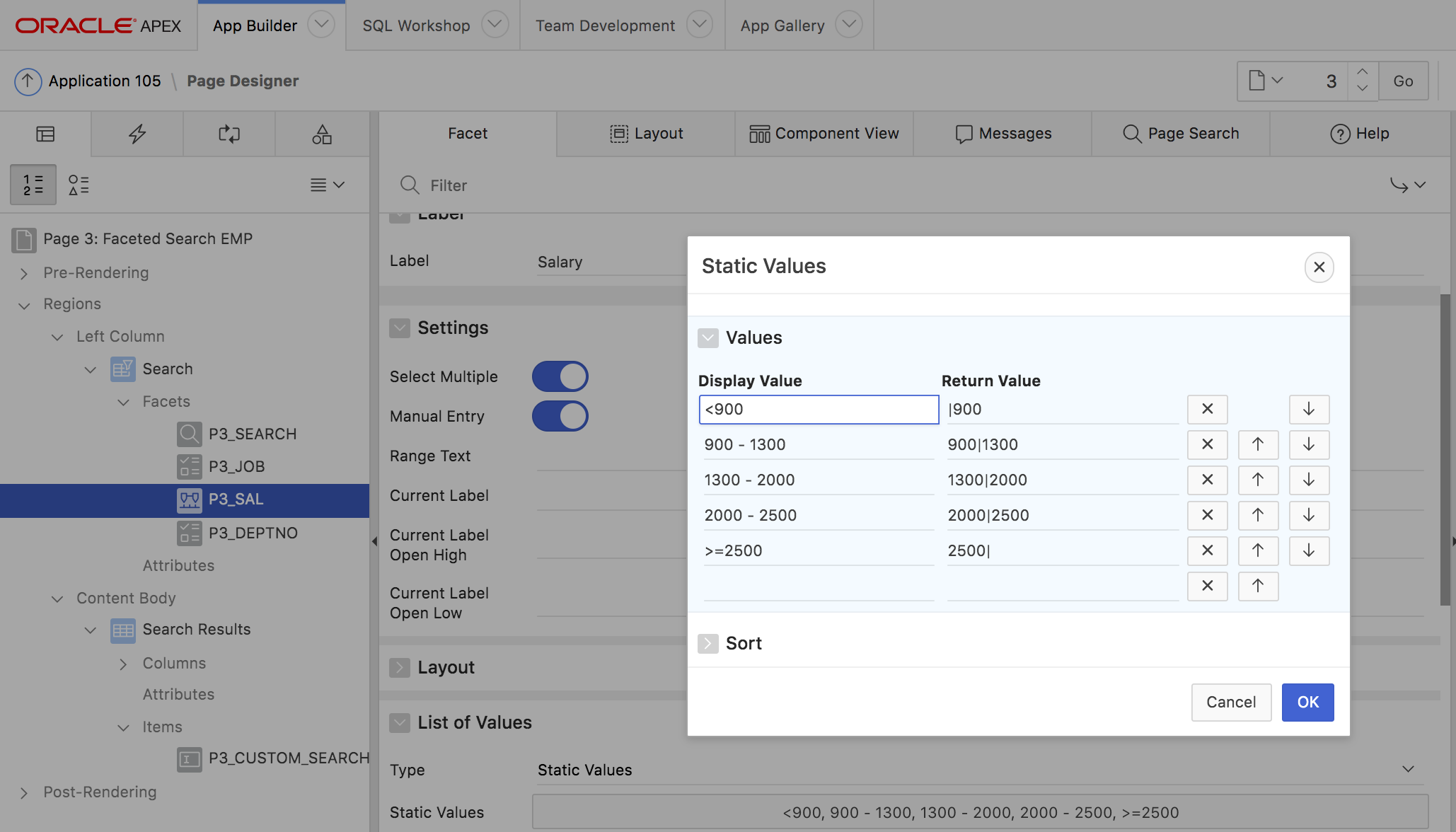
Fig. 11: LOV configuration for the Range Facet
Range facets also provide limited support for DATE and TIMESTAMP columns.
- The Create Page and Create Application wizards never generate range facets for DATE columns
- Only predefined ranges are supported; text fields or date pickers to manually pick a date as upper or lower boundary is not supported.
Given this, a range facet for the HIREDATE column of the EMP table can be manually created in Page Designer as follows:
- In Page Designer open the context menu of the Facets node in your Faceted Search region.
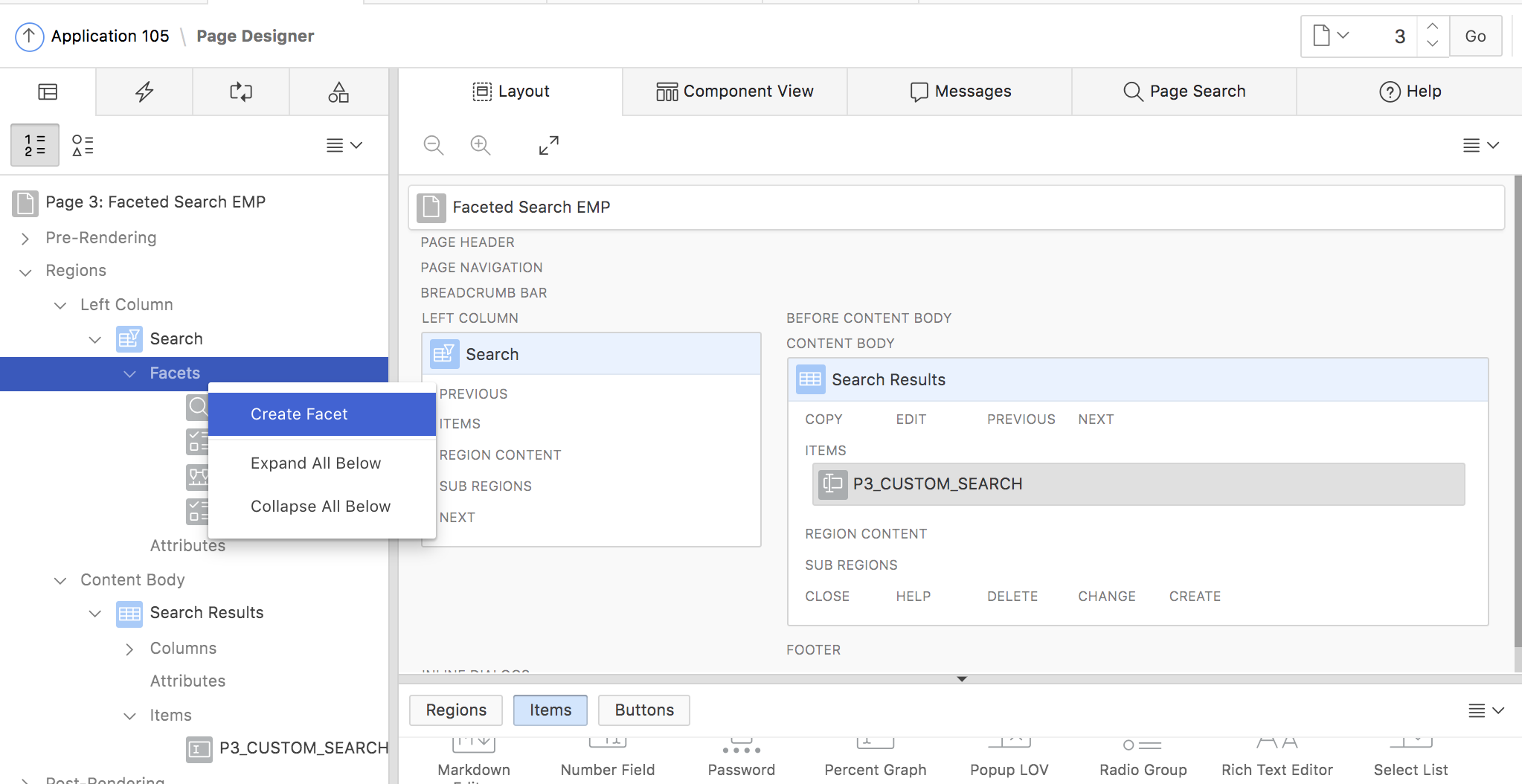
- Provide a name for the facet, e.g. PX_HIREDATE and pick a label.
- Choose Range as the facet type
- Map the facet to the HIREDATE classic report column and pick DATE as the data type
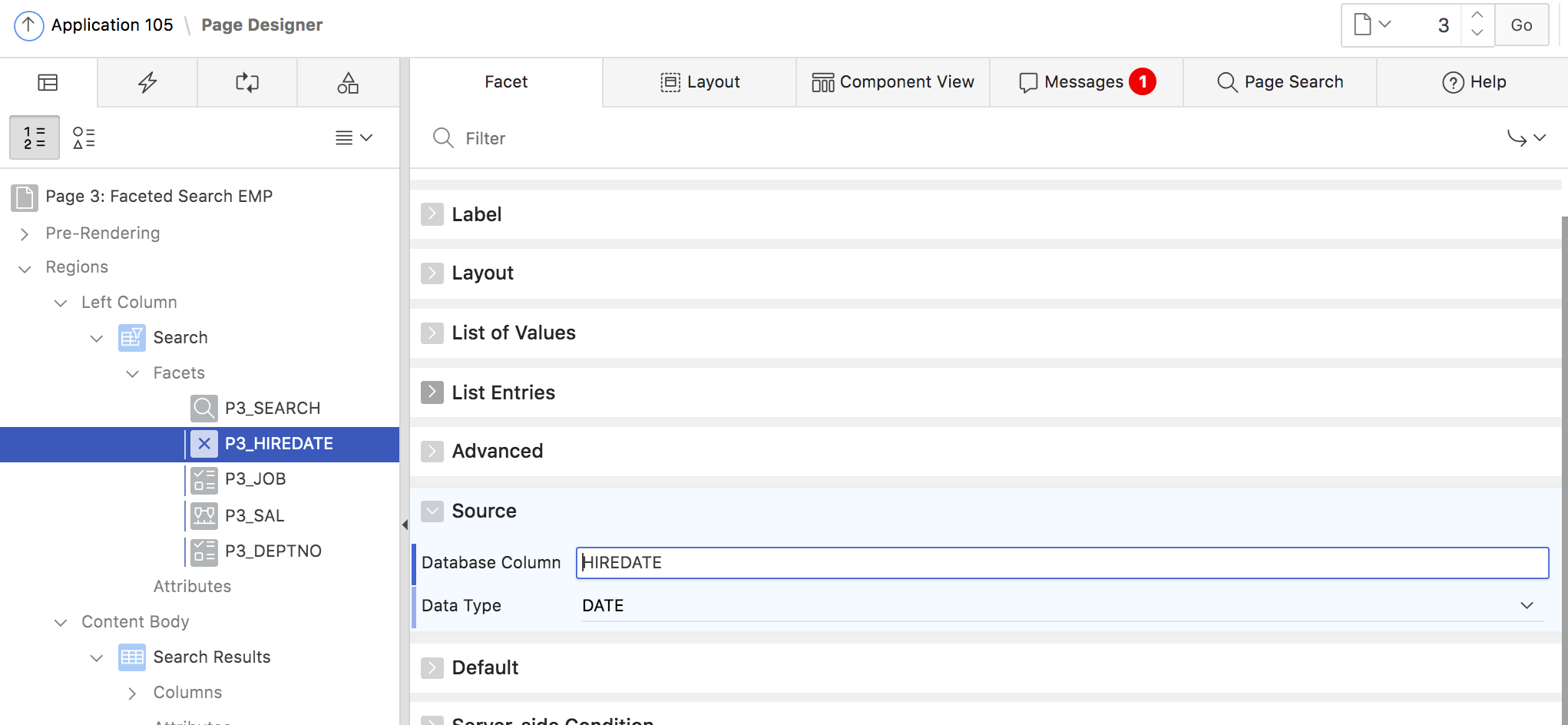
- In the Settings section, turn off Manual Entry. This is required – the page will throw an error message if Manual Entry is turned on for a range facet on a DATE column.
- Provide the LOV values. For DATE columns, use the “canonical date format” of YYYYMMDDHH24MISS. Use the pipe symbol (|) to separate lower from upper boundary. Provide the display value as appropriate. For the HIREDATE column of the EMP table, the LOV definition could look as follows:
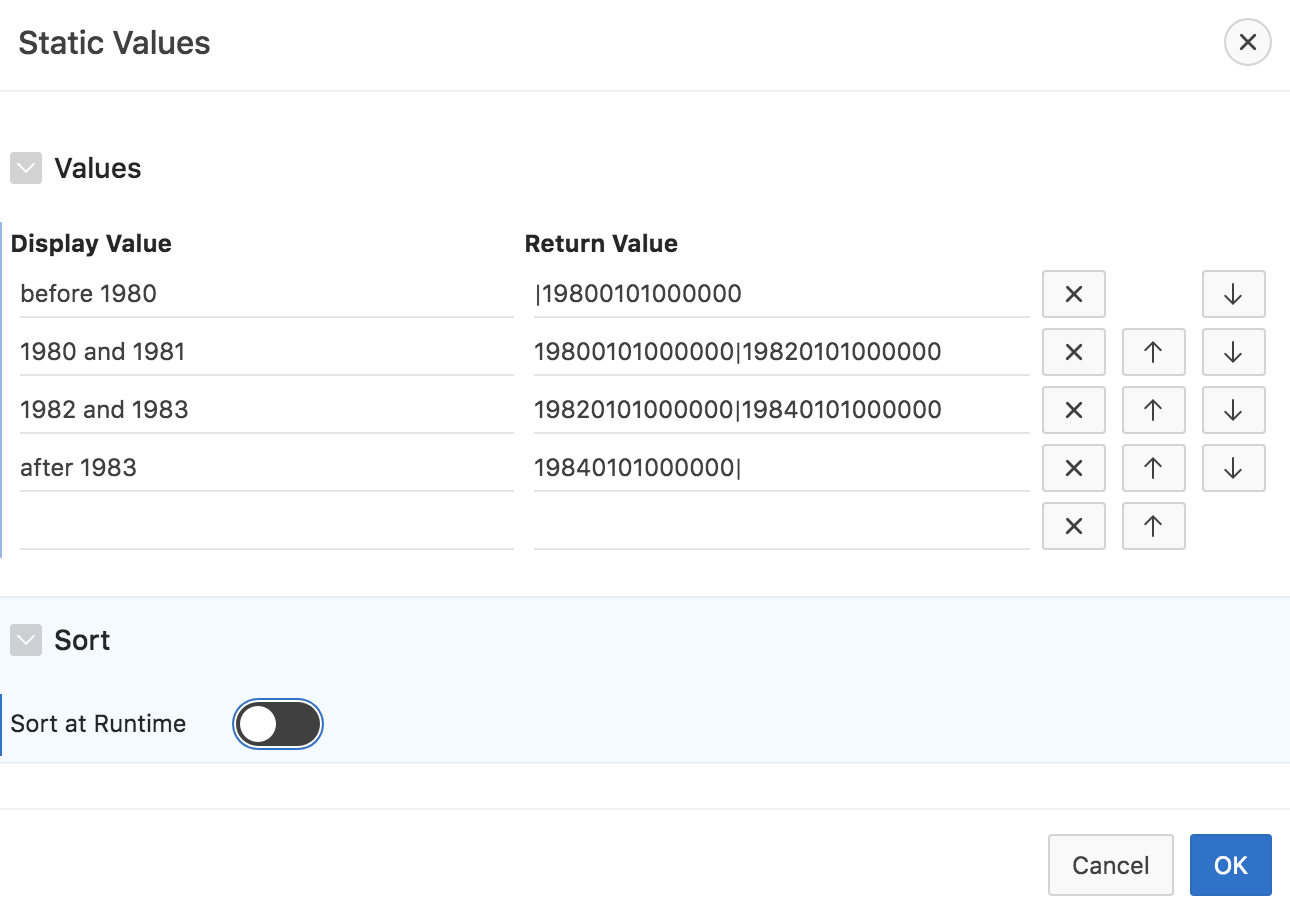
- Save your changes and run the page. You should now have another facet which allows to filter results on the HIREDATE column.
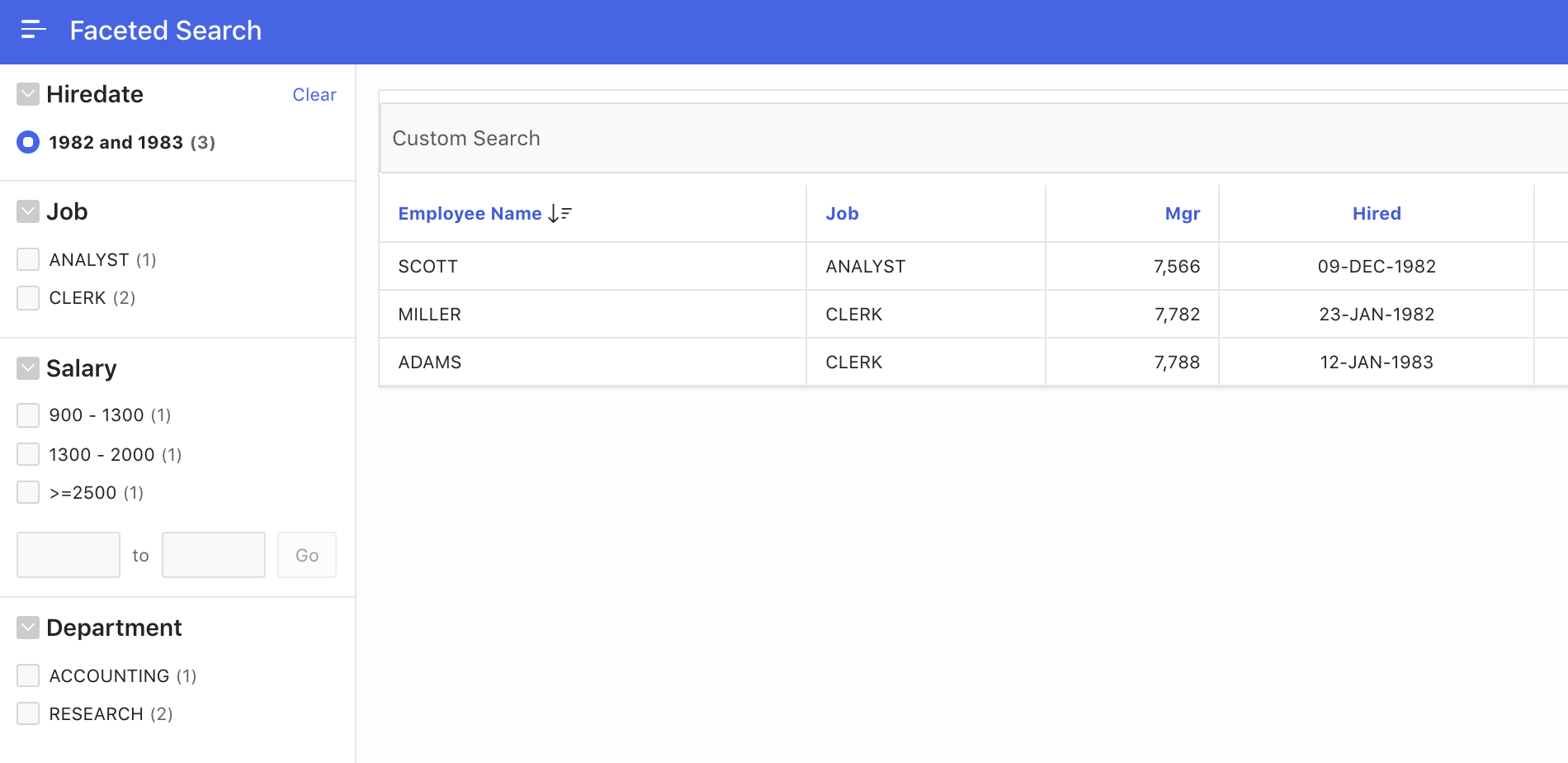
Using the same approach, you can also manually add more facets for other columns. Most important for each facet is typically the LOV to use. For good, usable facets, that list should not have too many values – hundredths of values would probably be too much – which end user can pick from these …?
Facet attributes
Page Designer allows to configure a number of facet attributes (fig. 12). These include:
- Compute Counts controls whether APEX should compute occurrence counts at all. If the report query as such is very expensive, and the occurrence counts are actually not needed, it can make sense to turn this off in order to save on computing resources. Note that in order to hide or disable facet values with no occurrences, the counts still have to be computed.
- Show Counts leads to the occurrence counts still being computed, but not being shown. APEX will just disable or hide facet values with no occurrences.
- Zero Count entries can be hidden or disabled. If disabled is chosen, APEX can always display them at the end of the list (Show Last).
- Show Selected First always reorders the list to show all selected values first.
- Client Side Filtering is usable if the select list returns more than just a few items. APEX generates a text field which allows to filter the list of facet items down to a small result set.
- Maximum Displayed Entries controls how many entries are shown. If the facet contains more entries, a Show More link will be added. Clicking this link reveals the complete list.
- The Facet Collapsible and Initially Collapsed settings control how the facet is displayed on page load.
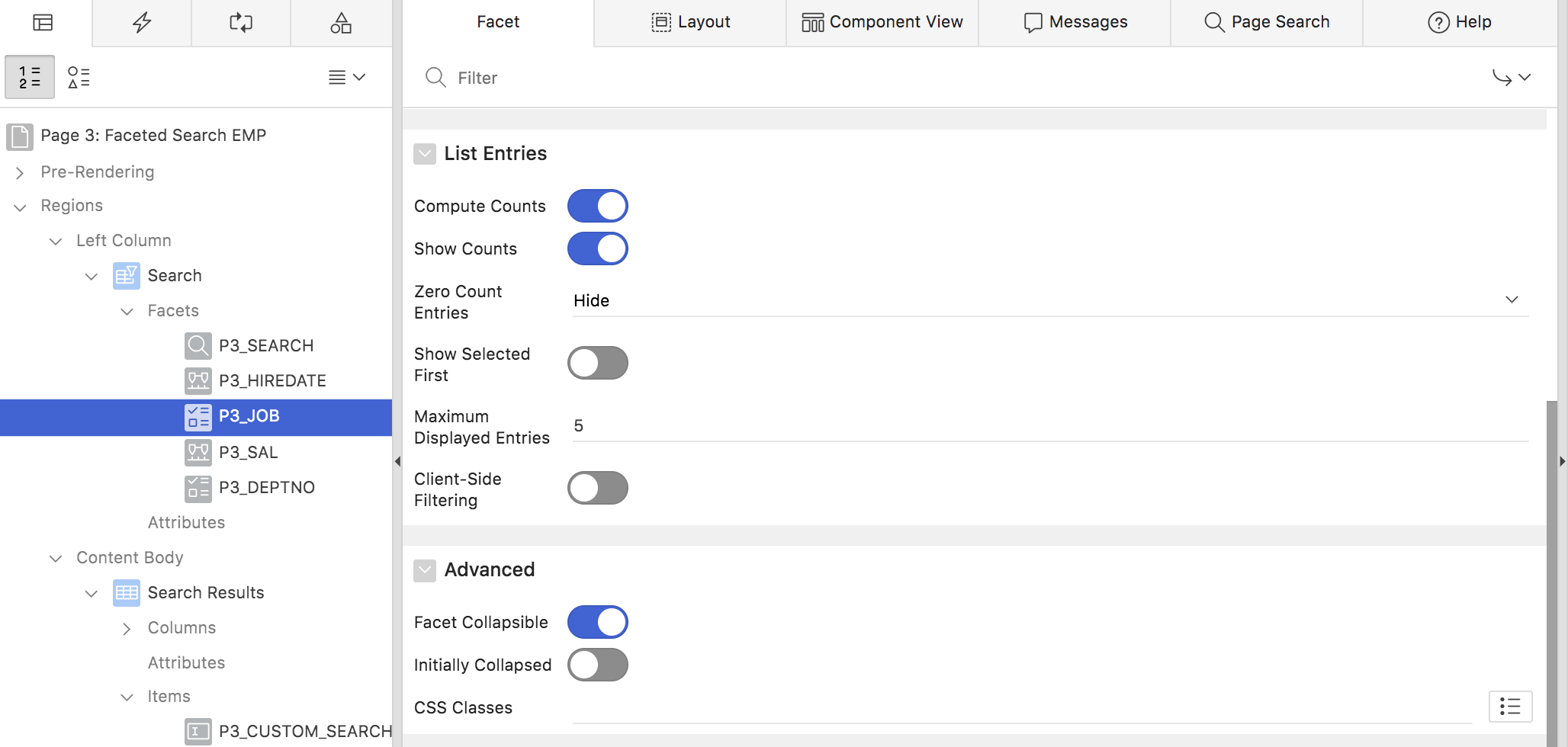
Fig. 12: Configurable Facet attributes in Page Designer
Faceted Search region attributes
A few faceted search attributes affect all facets, and are thus configured at the Faceted Search region level (fig. 13).
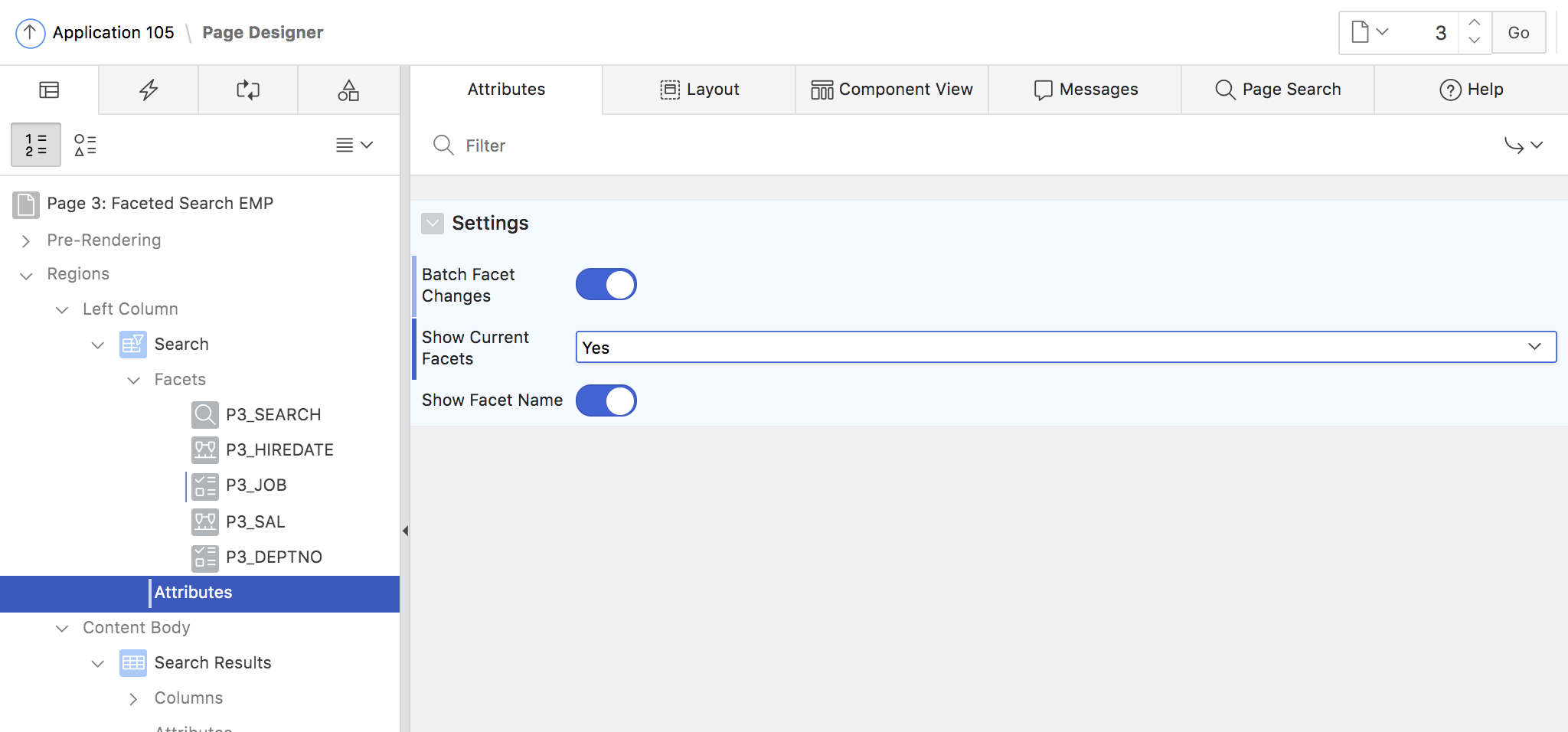
Fig. 13: Faceted Search region attributes.
The Batch Facet Changes attribute controls when the facets and the Classic Report refresh, after a change to one of the facets were made. By default, batch mode is turned off, and the refresh happens immediately. When turned on, a button is displayed after facets have been changed. Clicking the button leads to refreshing the report and facets.
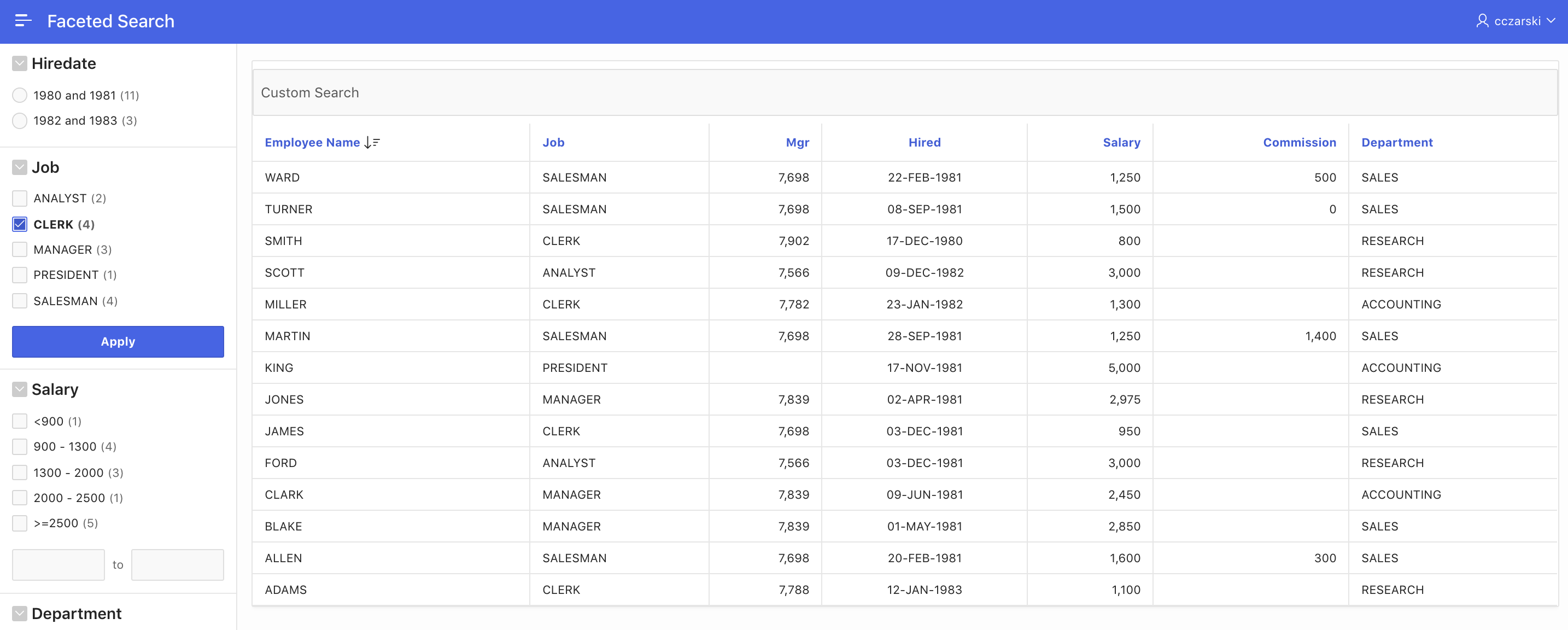 Fig. 14: Faceted Search with Batch Changes turned on.
Fig. 14: Faceted Search with Batch Changes turned on.
The Show Current Facets attribute controls whether the currently active facets are displayed as a summary above all facets or at a specific position on the page (fig. 15).
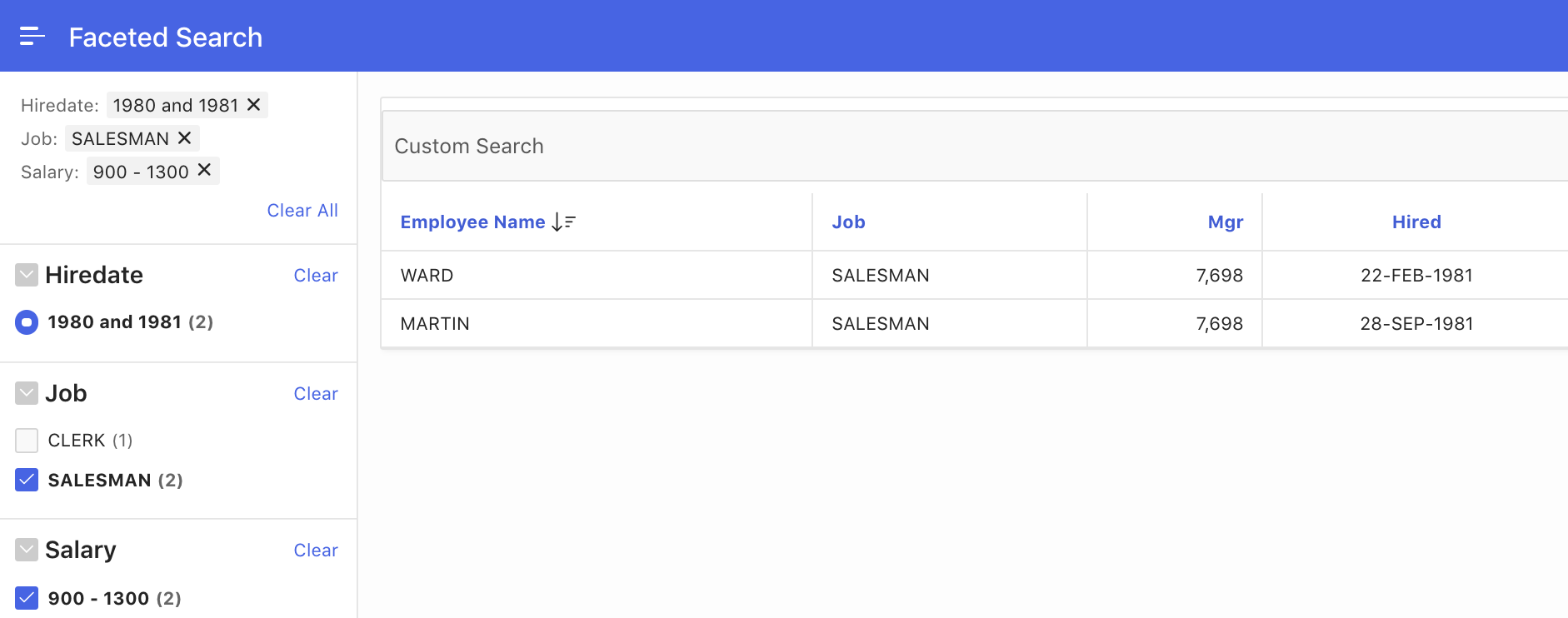
Fig. 15: The Show Current Facets option is enabled and in action.
Summary
The new Faceted Search feature in APEX 19.2 enables developers to provide fully functional faceted navigation with minimal effort. APEX does all low-level work of coordinating report and facet refresh, generating the required SQL queries to compute counts and integrating the facets with the report region. Developers just declare the report data source, the facets to use with the lists of values to get facet items from.
Faceted Search pages on local tables can easily be created using the Create Page wizard, which leverages the APEX dictionary cache in order to automatically generate facets. Custom SQL queries or remote data sources like REST services are supported as well. Since there is no dictionary cache for these, so facets must be created manually using Page Designer. However, the resulting faceted search pages can be as powerful for a REST service as for a local table. Fig. 16 shows a faceted search page working on a REST Service (USGS Earthquake JSON feeds: earthquake.usgs.gov).
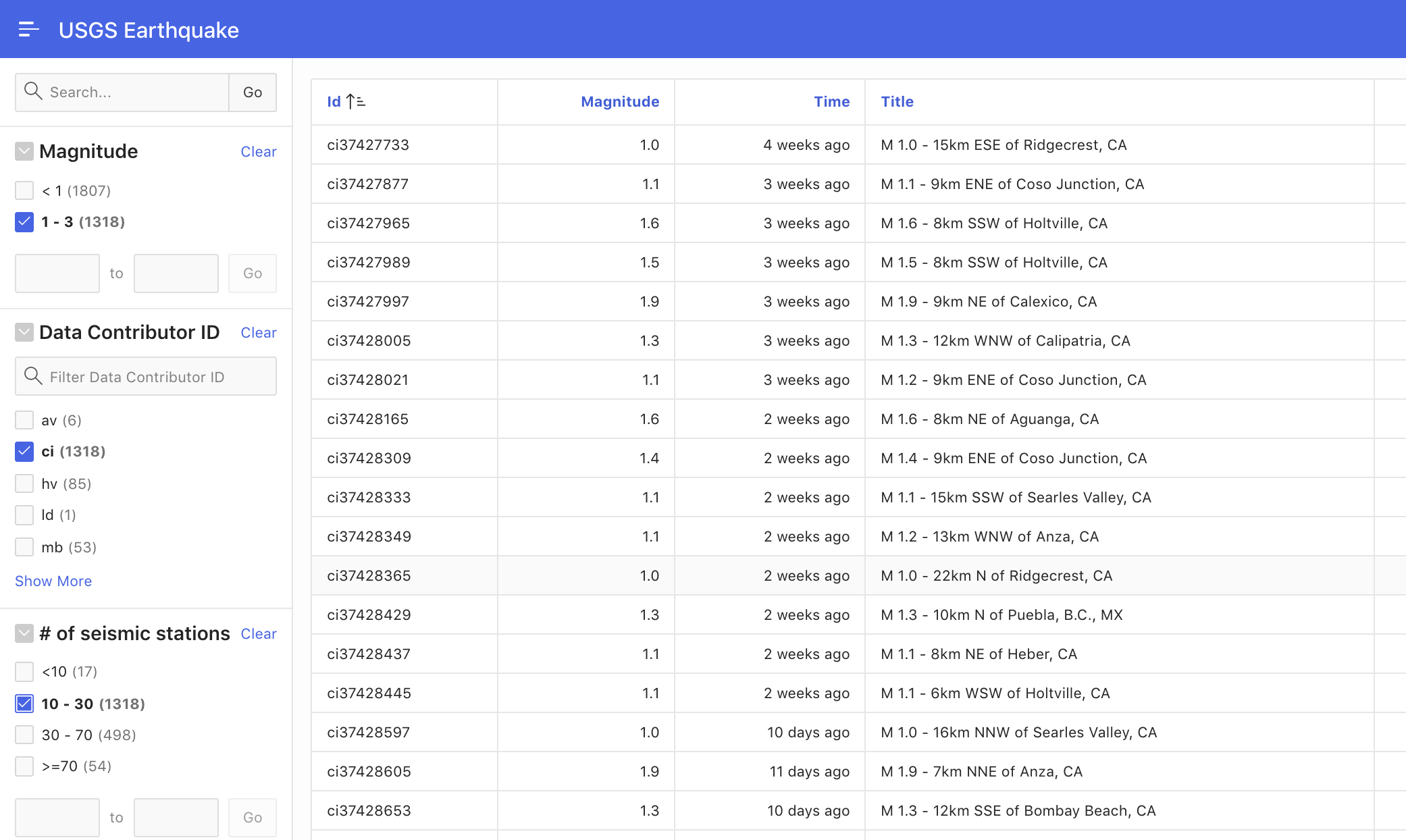 Fig. 16: Faceted Search using a REST service as data source.
Fig. 16: Faceted Search using a REST service as data source.
Try the faceted search feature out. It’s available today on the public APEX evaluation instance apex.oracle.com. Once APEX 19.2 is available for download, and your APEX installation has been upgraded, Faceted Search is available at your fingertips.
